Why is My Hair Falling Out: 15 Reasons & Treatments
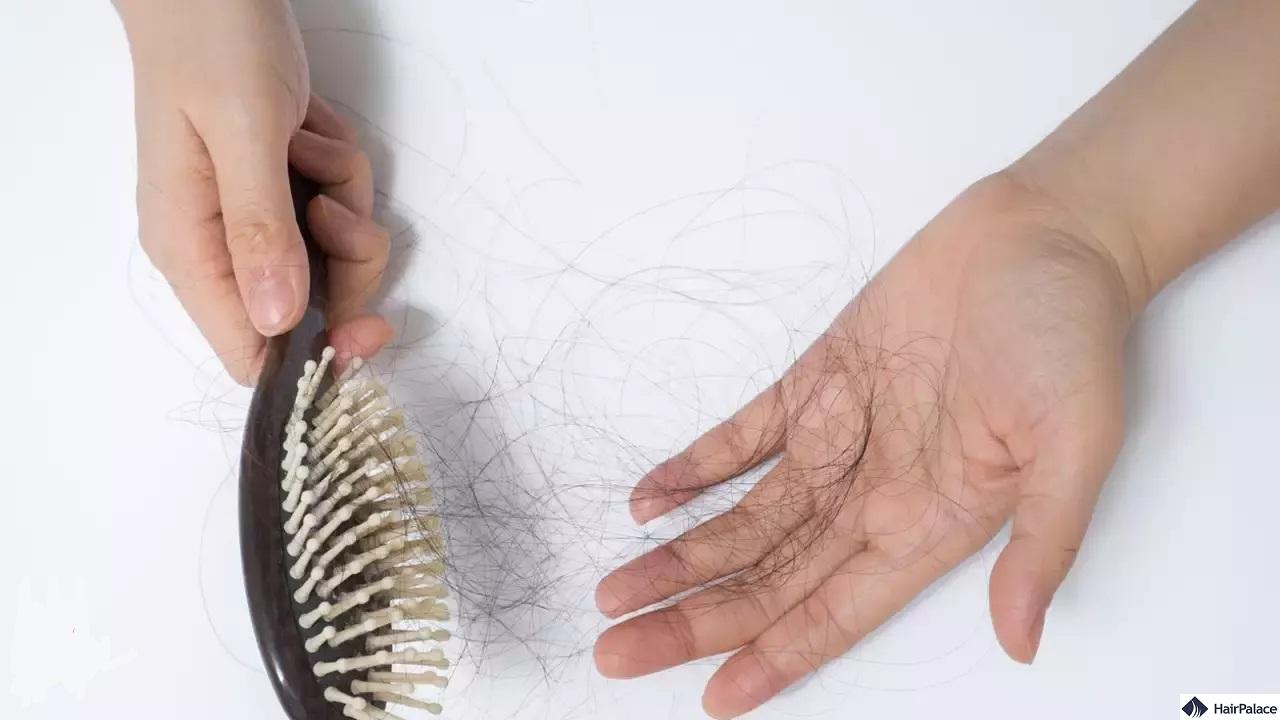
Hair loss is typically caused by genetics, hormonal changes, medical conditions or a scalp infection.
Nutritional deficiencies, stress, and certain medications can also contribute to the condition.
Over time, you might develop several obvious warning signs, that cause you to ask worrying questions.
Why am I losing hair? Do I have a health problem? Is there anything I can do to stop it?
We’re here to help you find those answers. This article will explore the most common causes of hair loss that you might be experiencing.
We’ll explain what their root cause is and highlight potential treatment options you might consider.
- Can hair loss be normal?
- Genetic conditions
- Hormonal changes
- Thyroid problems
- Medications
- Hair falling out stress
- Lupus
- Nutrition
- Telogen effluvium
- Anagen effluvium
- Traction alopecia
- Alopecia Areata
- Aggressive hairstyles
- Dramatic weight loss
- Age
- Other issues
- Treatment options
Is it normal for hair to fall out?
A certain amount of hair loss is a completely normal part of our everyday life.
It’s estimated that each person loses around 50 to 100 hairs without even noticing it.
This is perfectly normal as this amount can be easily reproduced by the natural hair growth cycle.
The problem starts when we start to lose more than 100 hairs each day and our body becomes unable to keep up with the rate of hair loss.
This can happen due to various factors such as stress, hormonal factors, medical conditions and even nutritional deficiencies.
Let’s take a closer look at the most common conditions responsible for hair loss.
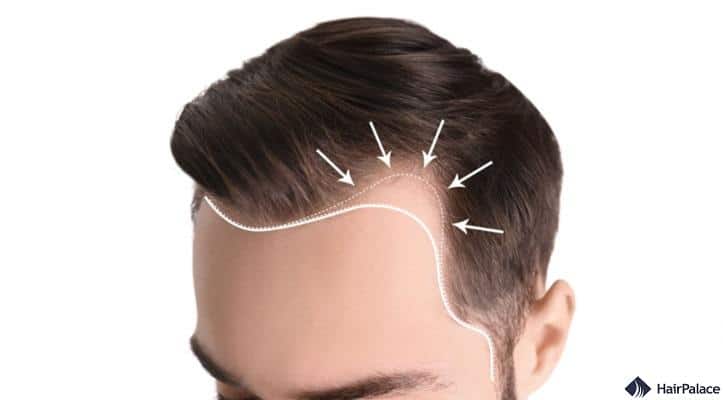
1. Androgenetic alopecia
Male pattern baldness or androgenic alopecia, is one of the most common reasons for hair loss in men worldwide.
This type of genetic hair loss is where certain genes predispose you to hair loss.
If someone in your family has experienced hair loss, this increases your chances of developing a hereditary hair loss condition.
Early signs of this type of hair loss include thinning and fine hair, a receding hairline, or hair falling out in clumps.
In women, the condition is known as female pattern hair loss.
Although not as severe as the male counterpart, this condition can still dramatically affect women, who will see an overall thinning of the hair, concentrating on the top and crown of the scalp.
2. Hormonal Fluctuations
Hormonal hair loss in women is a common occurrence.
Hormones are essential chemicals produced by the body to regulate various functions, including hair growth.
However, as we age, certain life stages can trigger hormonal imbalances that affect hair health.
For instance, hair loss in 50-year-old women can often be attributed to hormonal changes during menopause.
One key hormone involved is DHT (dihydrotestosterone), which can cause hair follicles to shrink, leading to hair thinning and premature hair loss.
Hormonal fluctuations during other stages of life can also result in hair loss.
These include early pregnancy hair loss, postpartum shedding, and hair loss due to the use of birth control pills.
In all these cases, shifts in hormone levels can disrupt the normal hair growth cycle, causing noticeable shedding or thinning.
This often leads to developing conditions such as frontal fibrosing alopecia. For men, these changes can be triggered with age.
3. Thyroid Issues
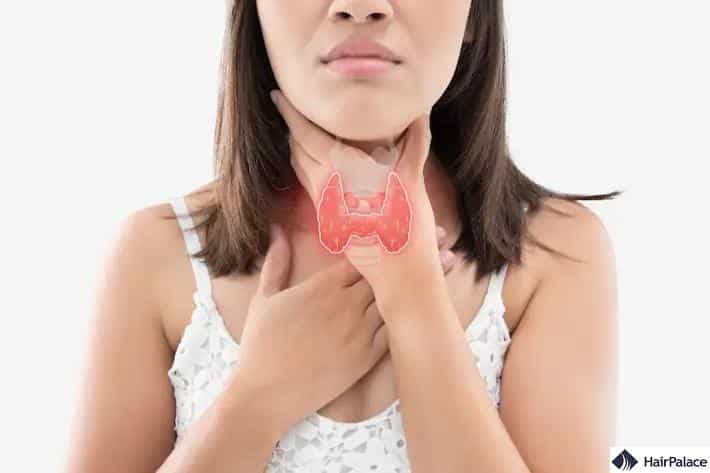
Your thyroid is one of the most important glands in the body, responsible for producing hormones that regulate your heart rate and body temperature.
If you suffer from thyroid disorders, this can result in thyroid hair loss.
Hyperthyroidism is when your thyroid over-produces hormones, while hypothyroidism is when there’s too little.
Both can trigger hair loss conditions and can be treated with medications.
Once you regulate your hormone production again, both your thyroid and hair loss problems should subside.
4. Medications
Some medications cause hair loss in certain patients as a side effect of treatment.
This kind of hair loss is often temporary, and once your course of treatment ends, your hair will gradually grow back.
Medications that often have this side effect include:
- Antidepressants
- Some oral contraceptives
- Thyroid-related medications
- Anticoagulants (blood thinners)
- Anticonvulsants (seizure medication)
- Beta-blockers
That said, every patient experiences medication differently, and you are not guaranteed to lose hair in the same manner as someone else.
If worried, consult with your doctor, as they may have an alternative recommendation that can help alleviate symptoms.
Never stop taking the medication without their advice.
5. High Stress Levels

Stress is something we all experience at some point in our lives.
But if you experience it for prolonged periods, stress can affect the quality and quantity of your hair.
It’s a vicious cycle – hair falling out causes high stress levels, which can cause even more hair loss.
But there are ways of breaking this cycle.
The following methods are a common way for many people to reduce stress levels and improve their lifestyle:
- Exercising each day, e.g., going for a short walk
- Practice mindfulness, including meditation and yoga
- Improve your diet by eating more vegetables and fruits
You should also try to avoid stressful situations whenever possible.
6. Lupus
Lupus is an autoimmune condition that can cause joint pain, rashes, fatigue, and hair loss.
Your immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue in your body, including hair follicles.
As such, the condition may trigger patchy lupus hair loss and skin lesions to develop across your scalp.
Certain medications used to treat the condition can also contribute to hair problems.
Lupus hair loss treatment usually aims to regulate the autoimmune condition, which resolves hair loss symptoms as well.
7. Nutrition Deficiencies

Like any other body part, your hair requires a certain level of nutrition to grow to its potential.
If it lacks specific vitamins or minerals, then it will grow short and thin and may fall out earlier than expected.
Examine your diet and try to improve the quality of the food you are taking.
Vitamins and nutrients to pay particular attention to include Vitamins A, B-12 (Cobalamin), B7 (Biotin), C, and D.
Your hair loss nutrition regime should also focus on healthy fats, copper, iron, zinc, and selenium.
If you are following a diet, consult with your doctor on possible deficiencies you might be experiencing.
They may recommend specific nutrition for hair loss and include vitamin and mineral supplements to improve your condition.
8. Telogen Effluvium
Your hair follows a strict hair growth cycle. Any disruption to it can cause significant complications, including sudden hair loss.
Telogen effluvium is defined as excessive hair shedding caused when you have substantial amounts of hair in the third phase of the growth cycle.
High-stress levels, certain medications, and thyroid issues can trigger the condition.
You may also experience telogen effluvium following major life events, like childbirth, surgery, or dramatic weight loss.
Though excessive shedding can feel alarming, hair will begin to grow back once the triggering event has been overcome.
9. Anagen Effluvium
Anagen effluvium is a condition where sudden hair loss occurs because the anagen (or growth) phase is affected.
Hair does not grow as long as it should and sheds earlier than expected.
Possible causes include chemotherapy, exposure to harsh chemicals and radiation, fungal infections, and autoimmune diseases.
Depending on its cause, treatment varies between patients, though most often, medication is prescribed to help stimulate and extend hair growth.
If undergoing chemotherapy, devices such as cooling caps can help reduce hair loss.
10. Traction alopecia
Repetitive stress or tension on hair can cause a hair loss condition known as traction alopecia.
Hair strands are pulled to such a degree that they stop growing, shed earlier than expected, and can lead to patches of baldness across your scalp.
Tight hairstyles that pull on hair, including tight braids, ponytails, cornrows, weaves, clip-in hair pieces, and even man buns can all contribute to this condition.
Try to wear hair as loose as possible, and vary your styles often to reduce consistent pressure on the hair.
In most cases, you can regrow hair after traction alopecia once you alleviate the stress from your hair follicles.
11. Alopecia Areata
As an autoimmune disease, alopecia areata causes your immune system to mistakenly attack hair follicles, causing sudden hair loss in the shape of circles.
This hair loss isn’t limited to the scalp and can take hold of eyebrows and eyelashes.
Though there’s no cure, you must see your doctor as soon as possible to alleviate symptoms and limit further hair loss.
Certain medications can be instrumental in helping stimulate follicles to grow hair again.
12. Aggressive hair styling practices
Aggressive hair styling is sadly one of the most common and easily avoidable causes of hair loss.
Using devices and tools like curling irons, hair straighteners, or dryers can expose hair to extreme heat, weakening it and leading to hair thinning and early shedding.
Additionally, using products with harsh chemicals, including shampoos, conditioners, and hair dyes, can cause hair loss.
Continued use will strip your hair of its natural defences, dry it out and weaken your hair follicles.
Finally, examine how you’re taking care of your hair.
Extreme physical trauma can be inflicted when brushing hair aggressively, especially when wet.
Instead, consider towel drying gently and only brushing hair when it has fully dried.
13. Dramatic weight loss
Any dramatic changes to your body, including weight loss, can have side effects and repercussions for your body.
This is because often, during weight loss, people follow strict diets, which can lead to nutritional deficiencies.
Additionally, the added stress of high-intensity physical exercise can increase sweating, leading to clogged hair follicles and increased hair shedding.
14. Age
We often think that age only affects women’s hair.
Menopause, for example, can cause significant hormone imbalances, leading to noticeable thinning and hair fall.
But men can also be a victim of hair loss with age, developing thinner, weaker hair that sheds earlier than expected.
Unfortunately, you can do little to prevent or combat this type of hair loss.
If you’re worried about hair loss as you grow older, you should visit your doctor as early as possible to start preventative treatments that maintain and preserve current hair.
15. Other Health Issues
Other health conditions contributing to hair loss include inflammatory bowel disease (IBS), diabetes, liver disease, or renal (kidney) failure.
You may also experience hair falling out after covid, or any other serious illness.
Additionally, certain skin conditions can negatively affect your scalp, causing hair follicles to become clogged or damaged.
These include infections like folliculitis or ringworm, dermatitis, and psoriasis.
What Treatments are Available?
Now that you’ve discovered the root cause of your thinning hair, you are undoubtedly curious about finding an effective hair loss treatment.
The first port of call for you to make is to visit your doctor.
They will be able to examine your scalp and hair and offer a professional diagnosis of your sudden hair loss.
They will recommend an appropriate treatment, including medication, lifestyle changes, or therapies.
That said, one of the most effective treatments for anyone losing hair is hair transplantation.
This highly effective procedure provides a permanent solution to male pattern baldness.
However, female hair transplants typically produce varying degrees of success.
A highly experienced surgeon will transplant healthy hair from your head and implant it into thinning areas, creating a natural-looking, fuller appearance.
The surgery has become so advanced that it boasts one of the highest success rates of any hair treatment.
FAQ
Some easy methods to help prevent further hair loss include:
● Avoid wearing tight hairstyles over prolonged periods (e.g., braids, cornrows)
● Don’t use heated styling tools (e.g., curling tongs, straighteners)
● Only use a soft hair brush. Use gentle strokes.
● Avoid harsh chemicals in treatments and hair dyes.
● Use shampoo and conditioners appropriate for your hair type.
● Use devices and therapies to stimulate hair growth, e.g., low-light therapy.
Below are five ways to monitor the rate of hair loss you are experiencing and ultimately find out if it’s excessive.
1. You find more hair on your pillow in the morning than usual
2. Your scalp becomes more visible
3. Your hair part widens
4. You are losing more hair after washing or brushing it
5. You lose several strands simply by running your hand through your hair
So long as your hair follicle remains intact, it can grow new hair. But if it has closed, is damaged, shrinks, or is inactive for a considerable period, hair may be unable to grow.
That said, even with permanent hair loss, you may achieve a thicker-looking head of hair by using different treatments to enhance existing hair and hide excessive shedding.
On average, people lose between 50 and 100 hairs a day.
To reduce hair fall, eat a balanced diet, avoid harsh hair treatments and chemicals, and practice gentle hair care.
Maintain a healthy diet, reduce stress, avoid harsh hair treatments, and use gentle hair care products.
Stress is one of the most common causes of hair loss.
Hair can grow back after falling out from the roots unless there’s a specific condition affecting the hair follicles.
The transplanted hair will fall out one month after the surgery. However this is completely normal, and new hair growth will occur shortly thereafter. Once this initial shock loss is over the implanted follicles will keep producing hairs until the end of your life.
Last medically reviewed on February 4th, 2025
- Nayak, Kashinath, et al. "Serum vitamin D3 levels and diffuse hair fall among the student population in South India: a case–control study." International journal of trichology 8.4 (2016): 160.
- Courtois, M., et al. "Periodicity in the growth and shedding of hair." British Journal of Dermatology 134.1 (1996): 47-54.
- Suad, H. H., and Gad Allah Modawe. "Investigation of diffuse hair fall case due to vitamin D deficiency: A Case report and literature review." Sudan Journal of Medical Sciences 13.2 (2018): 91-97.
- Agarwal, Soumya, et al. "Diffuse hair loss in females." Indian Dermatology Online Journal 10.1 (2019): 73.
- Kelly, Yanna, Aline Blanco, and Antonella Tosti. "Androgenetic alopecia: an update of treatment options." Drugs 76 (2016): 1349-1364.
- Nabahin, Amal, Alaa Abou Eloun, and Samy S. Abu-Naser. "Expert system for hair loss diagnosis and treatment." (2017).
- Price, Vera H. "Treatment of hair loss." New England Journal of Medicine 341.13 (1999): 964-973.


