What Causes Hair Loss? Full Breakdown in 2025
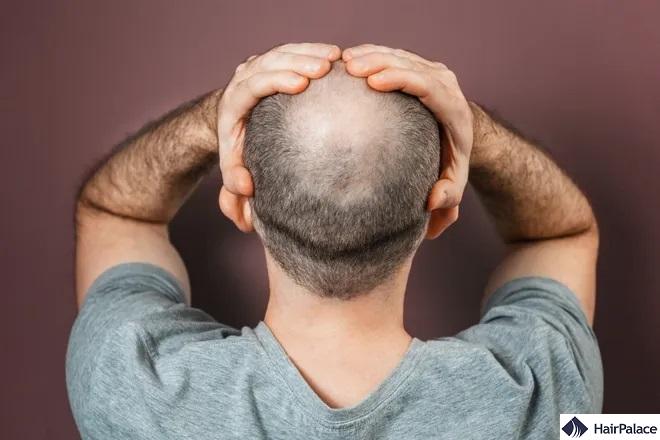

Under normal circumstances, we lose between 50 and 100 strands each day; our hair follicles around our body produce new hair to compensate for these losses.
But things don’t always go to plan, and our body fails to regrow new hair for one reason or another.
Over time, you might observe noticeable hair loss and overall hair thinning.
Unfortunately, there can be many reasons for extensive hair loss. But we’re here to help you find answers.
This article will explore everything you need to know about hair loss causes.
From the early symptoms you need to be aware of to the root causes of hair loss to highlighting the best available treatments, we’re here to guide you through this demanding time.
Hair loss symptoms
Many factors play a part in the complex issue that is hair loss.
One of the most common risk factors is genetics.
Hereditary conditions like male pattern hair loss (or female pattern hair loss) usually run in families and make up most cases.
However several factors can contribute to developing a condition at any age, including lifestyle choices, traumatic life events, changes in the level of male hormones, or an underlying medical condition.
Below are some of the most common symptoms and causes of hair loss to be mindful of:
1. Gradual thinning hair
Thinning hair is a common symptom most of us experience as we grow older.
Hair growth slows down, and you may experience overall thinning across your scalp.
In men, you might also experience a receding hairline, while women tend to experience a noticeable widening of their hair part.
Though not an exact science, the severity of age-related gradual hair thinning often stems from your genetics.
Review your family history and consider whether your parents experienced this type of hair loss. If yes, you are predisposed to hereditary hair loss.
2. Patchy hair loss
Hair loss isn’t always equal across your scalp.
Sometimes, it varies in shape and size, which can be a crucial symptom for diagnosing some specific conditions.
For example, small, patchy hair loss that is itchy and tender can be a strong sign of autoimmune illnesses like alopecia areata or alopecia barbae.
3. Sudden hair loss
Often, rapid hair loss occurs after a recent emotional or physical event in your life.
Your body shuts down certain functions, like hair production, in response.
Hair can fall out in large, often distressing clumps, worsening your emotional state even more.
This can be especially true with seasonal hair loss that can occur in autumn.
Thankfully, this is often a temporary hair loss condition, and once you recover from the cause, your hair will gradually regrow.
4. Full-body hair loss
Losing all your hair across your entire body can usually be attributed to specific medical treatments, like chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
Although you cannot stop this from happening, devices like cooling caps can help reduce the severity of your treatment on your hair.
Thankfully, once you finish these treatments, this type of hair loss will end, and hair will grow back.
5. Red, scaly or cracked skin on the scalp
Pay close attention to the nearby skin of the affected area, as it can prove vital in diagnosing the root cause of the problem.
If the skin is swollen, red, tender, scaly, and itchy, these types of hair loss may result from a fungal infection like ringworm.
Fungal or bacterial infections can be contagious, so visiting your doctor and beginning treatment as soon as possible is essential.
What causes hair loss?
There are various causes of hair thinning and hair loss in both men and women.
Below, we’ll examine the most common conditions and highlight their underlying cause.
Androgenetic alopecia
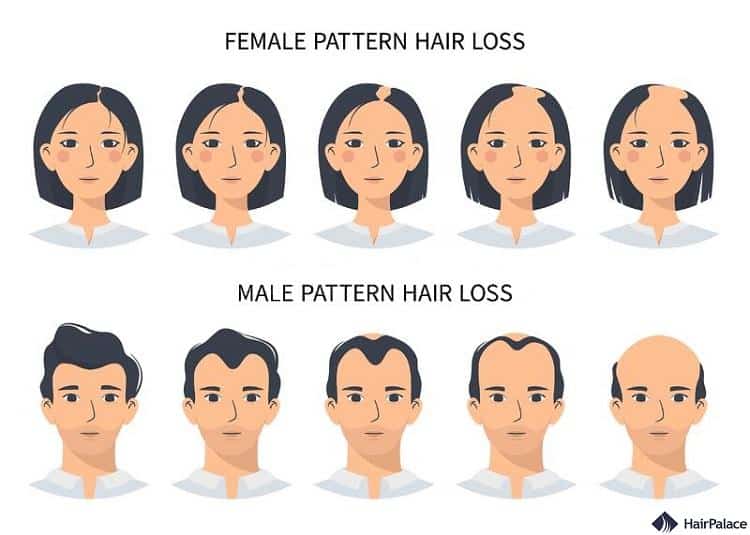

The reason of hair loss in male and female patients is almost always related to genetics.
Androgenetic alopecia is one of the most common hair loss conditions worldwide, affecting up to 50% of all people.
As a hereditary condition, it is thought that a combination of genetic factors and hormone imbalances is responsible for developing the illness.
People can begin to experience androgenic alopecia as early as puberty, though most only realize its existence when they grow older.
Causes of hair loss in men
The condition is known as male pattern baldness, resulting in a noticeable receding hairline that will eventually develop into a distinctive “M” shape.
Over time, the condition may result in total baldness.
Causes of hair loss in women
The condition is known as female pattern baldness. It differs in severity and rarely results in complete hair loss for women.
That said, you may notice thinning hair across their entire scalp and a widening to their hair part.
For this reason, a hair transplant for women typically yields worse results than its male counterpart.
Alopecia areata
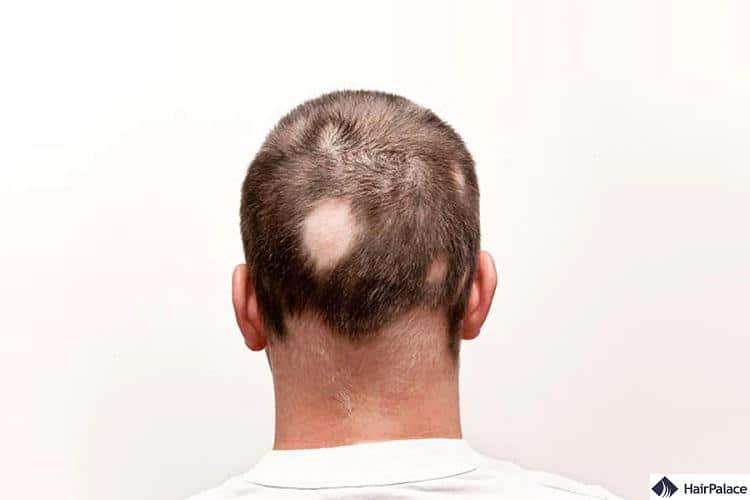
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disease that sees your immune system mistakenly attack healthy body parts, mainly hair follicles.
The core symptom of alopecia areata is quite easy to spot – sudden, patchy hair loss across the body, including the scalp, facial area, eyebrows, and eyelashes.
You may also develop red, brittle nails.
Hair loss from alopecia areata is usually temporary, and follicles can still grow back any lost hair.
Anagen effluvium
Anagen effluvium is an abrupt or rapid hair loss and is usually directly related to radiation and chemotherapies.
This is usually only a temporary hair loss condition, and you can expect hair regrowth once you finish treatment.
Telogen effluvium
Telogen effluvium is a common hair loss condition often triggered by immense emotional or physical stress.
Symptoms include hair thinning, scalp itchiness, and tenderness.
Telogen effluvium can also be triggered by hormonal changes in the body, including thyroid disease, birth control pills, pregnancy, and menopause.
It can also happen following surgery, an accident, or dramatic weight loss from medications such as Wegovy or Mounjaro.
In most instances, your hair will grow back on its own over several months.
Tinea capitis
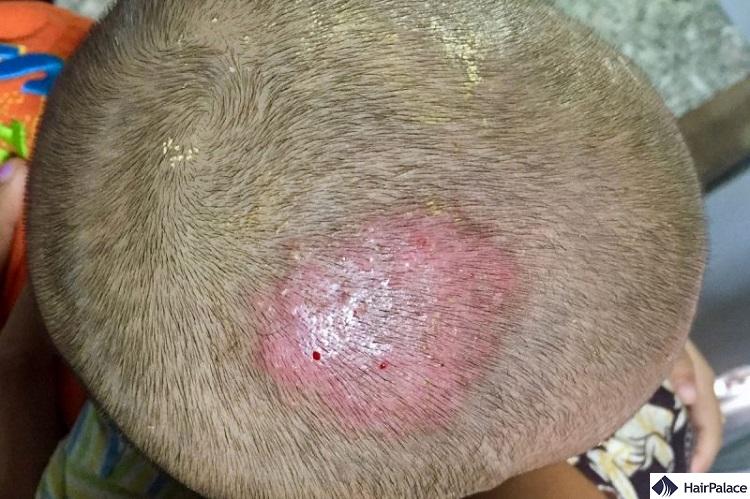
Tinea capitis is a ringworm of the scalp. It is caused by a fungal infection, is highly contagious, and can easily pass to other body areas.
Symptoms include small, circular bald spots that become itchy and inflamed.
Early treatment for tinea capitis is essential, as the inflammation can cause scarring and, thus, permanent hair loss.
Prescription antifungal medication is the best course of action.
Traction alopecia
When too much pressure is applied to your hair, and it begins to call out, you’ve developed a condition called traction alopecia.
It is a common side-effect of tight hairstyles such as braids, ponytails, cornrows, or tight buns.
Hair will only recover if you avoid wearing these styles and allow strands to recover.
Hair care
Specific hair treatments have been known to damage follicles to such a degree that they lead to permanent loss of hair.
Chemical treatments like perms, for example, alter the cell’s structure, changing its shape to produce wavy hair.
Similarly, bleaching breaks down beneficial fatty acids that once strengthened strands.
Although they may look great, both treatments severely damage the follicle.
Over time, repeated abuse can lead to significant, often permanent, hair loss, as the follicle cannot produce new strands.
Scalp infection
A scalp can become infected if fungus or bacteria enter the body through damaged skin or follicles.
The infection can cause bald spots to develop.
Treat the condition quickly with oral or topical antibiotics, and the hair will grow back in time.
Medication
Some medications have hair loss as a listed side effect. As such, taking them can limit or inhibit your scalp from producing new strands of hair.
If you are currently on a course of medication, examine the patient’s instructions for detailed guidance.
That said, never stop taking medication before bringing your concerns to your doctor.
Otherwise, you may experience serious complications.
Scarring alopecia
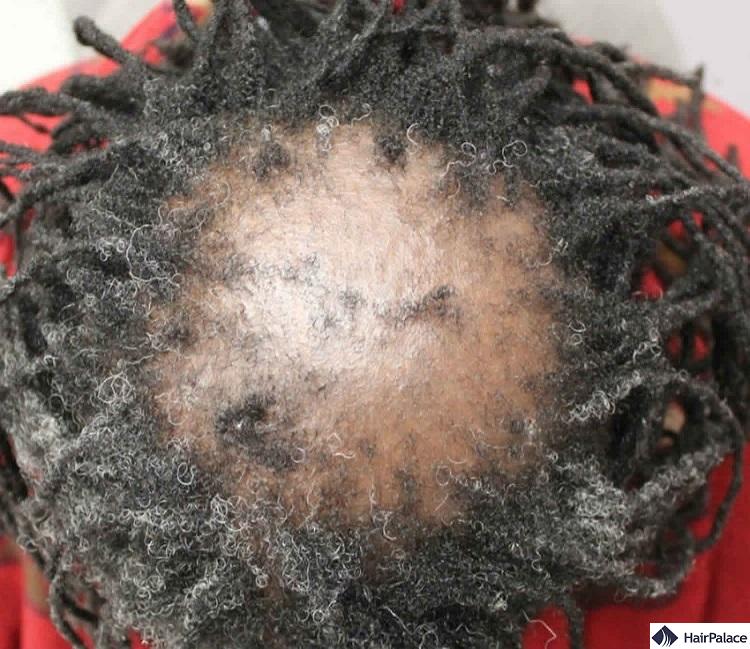
Scarring alopecia (cicatricial alopecia) is when hair follicles become permanently damaged.
As such, they cannot produce new hair and lie barren.
There are many causes of scarring alopecia, including severe inflammatory or autoimmune diseases.
Two of the most common conditions linked to scarring alopecia are Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia (FFA) and Central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia (CCCA).
The latter mainly affects women of African descent, and results in redness, skin scaling, itching, and raised bumps around the area of hair loss.
FFA on the other hand mainly affects women after menopause.
How do doctors diagnose hair loss?
Because there are several potential reasons for a hair loss condition, it’s highly recommended that you visit your doctor for a formal diagnosis.
Your doctor will do some tests, including a scalp examination and general health questionnaire, and ask about your family history.
They may send away lab tests to further diagnose your condition.
Only by finding the root cause of your hair loss can your doctor recommend the most appropriate treatments, medication, therapy, or surgical procedures.
What are the treatment options for hair loss?
Thankfully, there are several treatments available that can help alleviate and correct your hair loss symptoms.
These include:
1. Medication
Nowadays, over-the-counter and prescription medications promise to help combat hair loss conditions.
Arguably the two most popular include Minoxidil and Finasteride.
2. Medical procedures
Unfortunately, in some instances, medication won’t be enough to get the results you’re hoping for.
But there are alternatives you should consider.
Your doctor may recommend the following procedures:
- Platelet-Rich Plasma
- Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT)
- Hair transplant surgery
3. Alternative treatments
If medication and traditional medical solutions don’t work out, there are several alternative treatment options you can try, such as:
- Essential oils
- Scalp massage
How can I prevent hair loss?
There are certain lifestyle and styling choices you can make that can help protect and nurture your hair, while also reducing the amount you stand to lose each day.
These include:
Eat a healthier, nutritious diet
Vitamins and minerals are vital to a healthy body, allowing your cells to grow, repair, and reach their potential.
If you are deficient in a mineral or vitamin, one of the consequences could be accelerated hair loss.
For this reason, we highly recommend eating foods known to help hair growth, including antioxidants like beans, strawberries, blueberries, kale, spinach, and legumes.
These foods help create ideal growing conditions for your hair follicles.
Avoid sugary foods, alcohol, and foods containing preservatives and processed fats whenever possible.
Avoid hairstyles that pull on the hair
If your hair is vulnerable and delicate, you should avoid wearing tight hairstyles, like cornrows, tight ponytails, and braids.
These hairstyles can pull at your hair with enormous force and, if worn over prolonged periods, can lead to a condition known as traction alopecia.
We recommend that if you wear these styles, try to keep your hair as loose as possible and alternate between types to give your hair a chance to rest.
Avoid high-heat hair styling tools
Too much heat can harm hair, dehydrating strands and weakening it to such a degree that it falls out earlier than expected.
We recommend limiting your use of curling irons, hair straighteners, heated combs, and blow dryers to combat this problem.
If and when you need a heat-styling device, use its lowest setting possible and ensure hair is dry before use.
Use gentle hair care products
Anyone worried about hair falling out should limit or avoid entirely hair care products that contain harsh or potent chemical ingredients.
This is especially applicable to dyes, which often contain peroxide that can increase oxidative stress on hair and lead to early hair loss.
Substitute your hair care products for gentle, supportive alternatives, such as baby shampoo, so you can still clean your hair without irritating your scalp.
FAQ
Research from Harvard Medical School and similar institutions indicates that you cannot regrow hair lost due to hereditary conditions like male pattern baldness. Experts highly recommend early intervention, as you will likely continue to lose hair as you age.
In most cases, it’s due to hormone imbalances, e.g., pregnancy, and menopause, is reversible. So long as your hormone levels return to normal, hair has a high chance of growing back again.
Genetic hair loss is one of the most common conditions faced around the world. Unfortunately, there is currently no treatment that can prevent it. That said, you can try therapies to reduce or negate its severity.
Testosterone and estrogen are well known for contributing to hair loss. But thyroid issues and the stress hormone cortisol can cause early thinning and disrupt the natural hair growth cycle. By regulating your hormones, hair will grow back and you will prevent further hair fall.
Hereditary hair loss conditions like androgenetic alopecia (male or female pattern baldness) are perhaps the most common reason people lose hair.
Sudden and unexplained hair loss can result from several issues, including an underlying medical problem, hormone imbalance, too much stress, nutritional deficiency, and more.
If you notice that your hair falls out in a larger number, it may be time to visit your doctor.
Because Covid-19 can cause a high fever, undue stress, and anxiety, it’s not surprising that it can directly impact your hair. But some patients reported patchy baldness in the months following their recovery. Luckily, hair will grow back in time.
Certain vitamins are key ingredients to healthier hair. Vitamin D, in particular, is responsible for follicular stimulation, and if you are deprived of it, your hair will not grow to its potential and may shed early.
Certain studies claim that creatine increases your likelihood of suffering from hair loss. However, there is a lack of factual evidence to support this claim.
Vaping can potentially cause thinning. The nicotine and other chemicals in e-cigarettes can lead to reduced blood flow and damage to hair follicles, potentially resulting in a loss of hair. Additionally, the stress on the body’s systems caused by vaping can also contribute to this issue.
Chronic sleep deprivation may contribute to hair loss by increasing stress hormones (cortisol), disrupting the hair growth cycle, and weakening hair follicles.
Creatine itself has not been conclusively proven to cause baldness. However, there are concerns that it might increase levels of dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone linked to hair thinning in individuals genetically predisposed to male pattern baldness. More research is needed to establish a direct link between creatine supplementation and thinning hair.
Iron deficiency (anaemia) can lead to hair loss as iron is essential for oxygen transport and hair follicle health. Low iron levels can cause increased shedding and thinning, particularly in women.
A lack of Vitamin B12 can contribute to losing hair. Vitamin B12 deficiency can lead to reduced red blood cell formation and can negatively impact hair health, potentially resulting in baldness.
– Thinning hair on the scalp
– Increased shedding (more hair in brush, shower, or pillow)
– Receding hairline (especially in men)
– Bald patches or diffused thinning
– Weaker, brittle hair
– Slow hair regrowth
– Miniaturized (finer, shorter) hairs
Last medically reviewed on December 5th, 2025
- Sperling LC. “Alopeica.” In: Fitzpatrick JE, Morelli JG. Dermatology Secrets Plus (fifth edition). Elsevier, China, 2016:179-84.
- Do you have hair loss or hair shedding?https://www.aad.org/public/skin-hair-nails/hair-care/hair-loss-vs-hair-shedding
- Guo EL, et al. (2017). Diet and hair loss: Effects of nutrient deficiency and supplement use.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5315033/
- Malkud S. (2015). Telogen effluvium: A review.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4606321/
- Phillips TG, et al. (2017). Hair loss: Common causes and treatment.https://www.aafp.org/afp/2017/0915/p371.html


