Transgender Hair Transplant: What You Need to Know

If you’re a patient who identifies as transgender you might be considering transgender hair transplant surgery.
The surgery may be carried out to either thicken existing hair or restore hair in regions affected by male pattern hair loss.
For transgender women, this often involves feminizing the hairline by lowering it and creating a more rounded appearance.
For transgender men, hair transplants may be used to create a more masculine hairline or address hair thinning due to testosterone therapy.
Read on to find out everything you need to know about transgender hair surgery!
- What is it
- FtM hair transplant
- MtF hair transplant
- Masculine vs Feminine hairline
- Cost
- Who is a good candidate
- Non-surgical treatments
- Conclusion
What is a Transgender Hair Transplant?
A transgender hair transplant is a type of hair restoration surgery designed specifically for transgender patients.
It is designed to restore lost hair due to hormone replacement therapy, facial feminisation surgery, or other hormone treatments.
This type of surgery is different from regular hair transplantation, as it focuses on creating a more feminine hairline and restoring hair density in areas where hair has been lost due to hormone treatments.
The procedure involves taking healthy follicles from the back and sides of the head and transplanting them to the desired area of the scalp.
Transplanted hairs will grow naturally and will not be affected by hormone treatments.
It is typically performed under local anaesthetic, and the patient can expect to be back to normal activities within a few days of the procedure.
Transgender hair transplant has become increasingly popular over the years, as more transgender patients seek out this type of surgery to help them feel more comfortable in their skin.
It is important to note that the results of the procedure can vary depending on the patient, and that the patient should discuss their individual needs and expectations with their surgeon prior to the procedure.
Female to Male Hair Transplant
In the case of an FtM transition, male hormones can change the way you look which can include changes to your hair.
Over time you may develop transgender male pattern baldness. Male pattern hair loss happens due to a male hormone called DHT or dihydrotestosterone.
This hormone attaches itself to certain receptors on the scalp which causes hair follicles to shrink over time.
The process eventually renders the follicles incapable of supporting any new hair growth.
There is currently no cure for male pattern baldness.
However, there are several hair loss medications such as finasteride or minoxidil that can slow down or halt its progression.
However, none of these treatments provides a permanent solution for baldness.
FUT and FUE hair transplants, on the other hand, can provide a lasting solution for hair loss and restore your full head of hair.
The surgery results in a more natural appearance and an even hairline.
When it comes to FtM transitions, beard and eyebrow transplants may also be used to help create a more masculine appearance.
Hormone therapy will result in a certain amount of eyebrow or beard growth. However, in most cases, the hair that grows can appear patchy or not as full as you’d want.
Male to Female hair transplant
The male-to-female transition process can result in the opposite effect.
The shift in your estrogen levels may counteract the effects of the DHT hormone.
In case you experienced male pattern baldness before transitioning, you may have bald spots or an MtF receding hairline.
This can seriously hinder the results of your gender reassigning surgery as your head will still resemble that of a receding male.
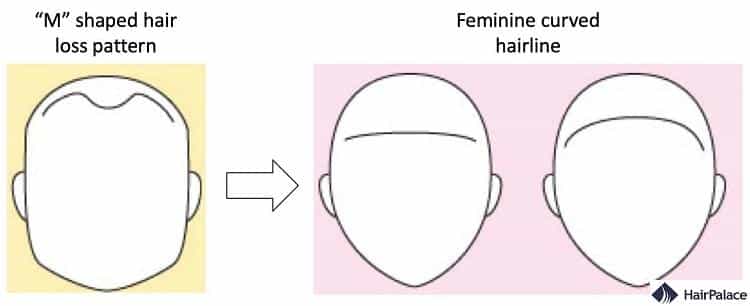
Most men who experienced hair loss have an “m” shaped hairline.
This can be transformed into a feminine curved hairline during an MtF hair transplant surgery to give a more feminine appearance.
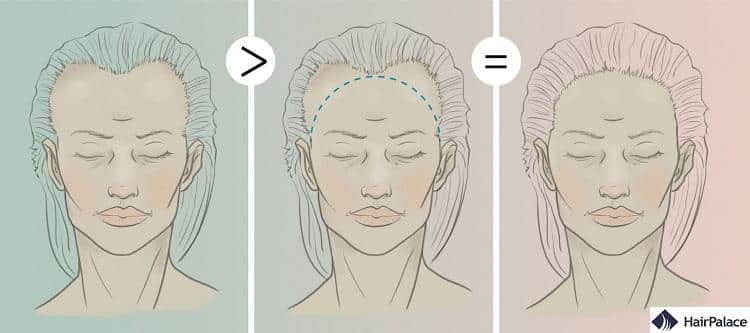
What are the differences between a masculine and a feminine hairline?
Understanding the differences between feminine and masculine hairlines is essential for the construction of a natural appearance for the patient.
The main differences lie in the shape of the hairline, the way hairs flow and the ageing pattern.
Feminine hairlines are generally lower whereas masculine hairlines tend to be further back.
As males age, their hairline usually recedes to some extent, and their foreheads become more pronounced.
Whereas women rarely go through this experience.
Women may also suffer from hair loss, but it tends to be more sporadic in nature and it isn’t restricted to a specific region.
Males typically develop an “M” shaped hairline as their temples recede. While females maintain an oval-shaped hairline for most of their life.
Transgender hair transplant cost
Transgender hair transplantation surgery costs can vary greatly depending on the individual’s needs and the technique used for the procedure.
Generally, transgender hair transplants can cost anywhere from £3,000 to £12,000, depending on the complexity of the procedure and the number of grafts necessary.
The amount of hair that can be transplanted depends on the amount of donor hair available.
The cost of a transgender hair transplant also depends on the medical facility performing the procedure and the experience of the surgeons.
Some facilities may offer discounts or payment plans to help offset the cost of the procedure.
Hair Transplant for Transgender Patients: Who is a good candidate?

A good candidate for a transgender hair transplant is someone who has been on hormone replacement therapy (HRT) for at least one year.
This candidate should also be healthy and have realistic expectations about the results of their hair transplant.
A transgender hair transplant is a specialized procedure that requires an experienced surgeon who is familiar with the unique needs of a transgender patient.
The potential candidate should make sure the surgeon has experience in performing transgender hair transplants and ask for before-and-after photos.
A qualified hair transplant surgeon should discuss the patient’s options and provide an individualized treatment plan.
Alternative non-surgical hair loss treatments
It is generally advised to try out non-surgical hair loss treatments before deciding to undergo surgery. They are much less invasive and may provide better results for certain types of hair loss.
The efficacy of these treatments will largely depend on how advanced your hair loss is.
Stimulating treatments such as Minoxidil can greatly increase the vitality of your hair follicles.
However, if you already have large bald spots then this treatment won’t do much for your condition.
Another successful hair loss treatment, Finasteride works by halting the balding process. It does so by blocking the enzymes that convert testosterone into DHT.
This treatment also works best at the early stages of hair loss, but just like minoxidil, it won’t lead to the creation of new hair follicles.
Conclusion
The shape and position of male and female hairlines are important gender traits.
Certainly, hairpieces or wigs can be worn to cover this male pattern baldness, but these “solutions” are simply not the permanent solution most people want.
Transgender hair transplants can help individuals who are transitioning from one gender to another to achieve a more cohesive appearance.
We recommend exploring your options to ensure that you find the right doctor and clinic that can help you achieve your aesthetic goals.
Last medically reviewed on July 30th, 2025
- Gender-affirming hair procedures by Jeffrey Epstein MD, January 18,2023https://www.optecoto.com/article/S1043-1810(23)00004-0/fulltext
- Marks DH, Hagigeorges D, Manatis-Lornell AJ, Dommasch E, Senna MM. Hair loss among transgender and gender-nonbinary patients: a cross-sectional study. Br J Dermatol. 2019 Nov;181(5):1082-1083. doi: 10.1111/bjd.18099. Epub 2019 Jul 21. PMID: 31049935.https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31049935/
- Gao JL, Streed CG Jr, Thompson J, Dommasch ED, Peebles JK. Androgenetic alopecia in transgender and gender diverse populations: A review of therapeutics. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021 Oct 28:S0190-9622(21)02574-3. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2021.08.067. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 34756934.https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34756934/
- ISHRS: 2025 Practice Census Resultshttps://ishrs.org/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/report-2025-ishrs-practice-census_05-12-25-final.pdf


