Rejected Hair Transplant: Why Does it Happen?

A rejected hair transplant occurs when the body’s immune system attacks the transplanted hair follicles, leading to the failure of the transplant.
This can result from improper donor-recipient matching, poor surgical technique, or individual immune responses.
Symptoms of a hair transplant gone wrong may include redness, swelling, pain, and hair loss at the transplant site.
Addressing a rejected transplant typically involves a medical intervention to manage inflammation and potential re-transplantation or alternative hair restoration methods.
Find out more about failed hair transplants and learn how to fix your newly transplanted hair!
- What affects the success of a hair transplant?
- 7 reasons for hair transplant rejection
- What can you do about hair transplant graft rejection?
What affects the success of a hair transplant?
The success of a hair transplant can be influenced by a variety of factors, both related to the hair transplant procedure itself and the individual undergoing the treatment.
The density, quality, and availability of hair in the donor area are crucial.
A robust donor area can provide healthy grafts that are more likely to survive and yield a successful hair transplant.
The expertise of the surgeon performing the transplant is also paramount.
Skilled hair transplant surgeons can ensure the grafts are handled delicately and placed in a way that looks natural.
There are different hair transplant methods, such as Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE).
Each has advantages and potential drawbacks, and the choice of technique can impact whether you’ll have a rejected hair transplant.
A full scalp examination is also key to ensure there are enough healthy hair follicles in the donor area.
Inadequate donor site density and quality can contribute to hair transplant failures.
Lastly, hair transplant patients must follow proper aftercare following the hair restoration surgery.
This can greatly improve the quality of hair grafts and help with longevity.
This also includes following a certain lifestyle after the procedure.
Refraining from smoking and eating a balanced diet can help you avoid hair transplantation failure and promote your overall health.
7 reasons for hair transplant rejection
Hair transplant rejection is not common in the traditional sense of organ transplant rejection.
Since the tissue is from the same individual, the immune system does not recognize the transplanted follicles as foreign.
This means there is no immune-mediated rejection as seen with organ transplants.
However, hair transplant rejection can still occur due to malpractice during the surgery or preexisting health issues.
1. Poor Graft Handling
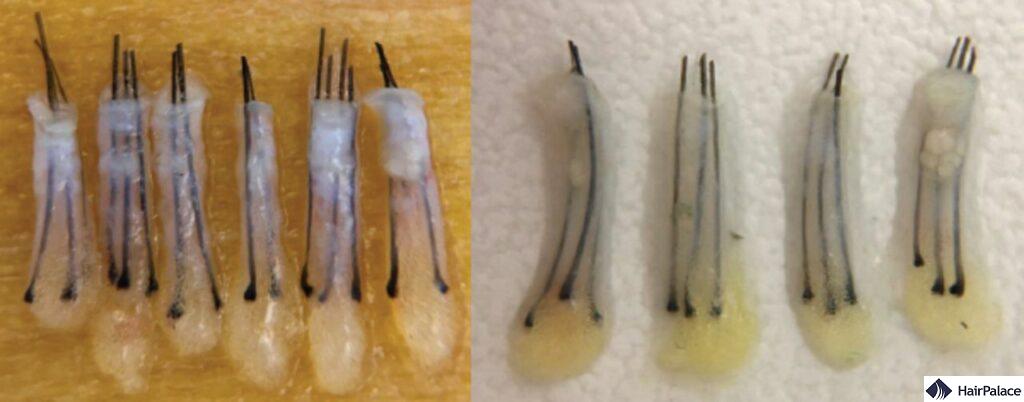
If the hair follicles (grafts) are not handled carefully during the hair transplant surgery, they can get damaged, leading to poor hair growth.
The skill and experience of the surgeon play a critical role in ensuring the viability of the grafts.
2. Infection
Infection at the transplant site can compromise the success of the transplant, affecting the survival of the transplanted follicles.
3. Poor Blood Supply
Many hair transplants fail due to poor blood supply to the transplanted hair follicles.
Areas with poor blood circulation might not support the newly transplanted grafts, leading to hair transplant failure.
4. Scarring
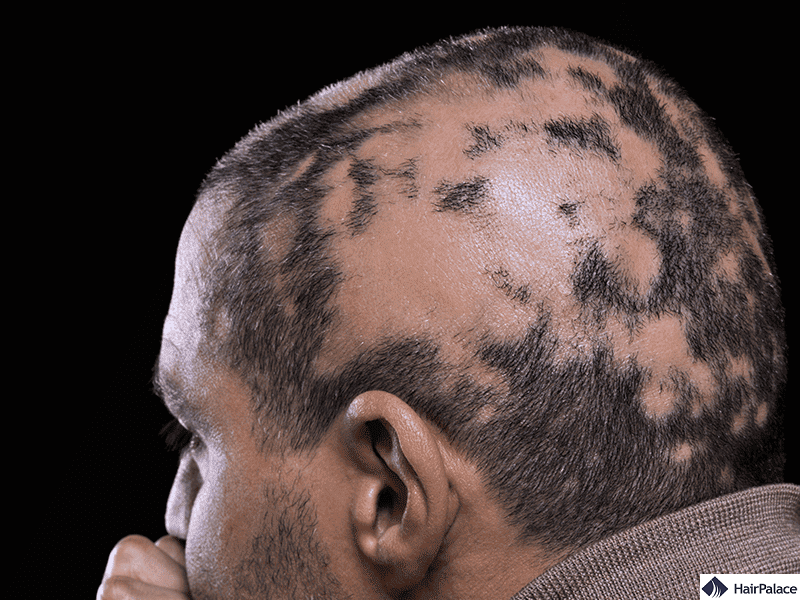
Excessive scarring from the procedure can impact the ability of the transplanted hairs to grow through the skin.
5. Folliculitis
Sometimes, inflammation around the hair follicles, known as folliculitis, can occur after a transplant, which can affect the growth of transplanted hair.
6. Shock Loss
This refers to the temporary loss of the existing natural hair around the transplant site due to trauma from the surgery. Although this is usually temporary, it can be distressing.
7. Improper Post-Operative Care
Not following the surgeon’s post-operative care instructions can lead to complications that affect the outcome of the transplant.
What can you do about hair transplant graft rejection?
Most people don’t experience a rejected hair transplant. However, hair transplant graft rejection can still occur if the quality of your treatment is subpar.
Thankfully, several other treatments for hair loss can save your hair transplant and fix any problems that may have occurred.
2nd hair transplant
Yes, having a second hair transplant is possible if the first one did not yield the desired results or failed due to various reasons, such as poor graft survival or unsatisfactory hair density.
Before proceeding with a second transplant, it’s crucial to understand the reasons behind the failure of the first procedure.
A thorough evaluation by a qualified and experienced hair transplant surgeon can determine your suitability for a second hair transplant operation.
Factors like the availability of donor hair, scalp condition, and overall health will be considered.
The second procedure often involves refining the results of the first transplant, enhancing density, and addressing any aesthetic concerns.
Scalp micropigmentation
Scalp Micropigmentation (SMP) is a non-surgical treatment that involves applying tiny, tattoo-like pigment dots to the scalp to mimic the appearance of hair follicles.
It can fill in areas between transplanted hairs to create an illusion of fuller hair density or camouflage scars from FUT hair transplant surgery.
SMP is particularly effective for adding visual depth to thinning areas and improving the overall aesthetic outcome by blending the transplanted hair with the natural hairline.
Last medically reviewed on July 23rd, 2024
- Perez-Meza D, Leavitt M, Mayer M. The growth factors. Part 1: clinical and histological evaluation of the wound healing and revascularization of the hair graft after hair transplant surgery. Hair Transplant Forum Int. 2007;17:173–5.https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Hair+Transplant+Forum+Int&title=The+growth+factors.+Part+1:+clinical+and+histological+evaluation+of+the+wound+healing+and+revascularization+of+the+hair+graft+after+hair+transplant+surgery&author=D+Perez-Meza&author=M+Leavitt&author=M+Mayer&volume=17&publication_year=2007&pages=173-5&
- Petrungaro P. Hard and soft tissue healing and maturation in the reconstruction of the maxillary pneumatized sinus. Contemporary Peridontic and Implantology. 2001https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Contemporary+Peridontic+and+Implantology&title=Hard+and+soft+tissue+healing+and+maturation+in+the+reconstruction+of+the+maxillary+pneumatized+sinus&author=P+Petrungaro&publication_year=2001&
- Perez-Meza D. Clinical and microscopic revaluation of the hair transplant graft. In Programs and abstracts 8th Annual ISHRS meeting, Kona Hawaii. 2000 https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=In+Programs+and+abstracts+8th+Annual+ISHRS+meeting,+Kona+Hawaii&title=Clinical+and+microscopic+revaluation+of+the+hair+transplant+graft&author=D+Perez-Meza&publication_year=2000&
- ISHRS: 2022 Practice Census Resultshttps://ishrs.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/04/Report-2022-ISHRS-Practice-Census_04-19-22-FINAL.pdf


