Lupus Hair Loss: Prevention and Treatment Options

Lupus (otherwise known as systemic lupus erythematosus, or SLE) is a condition causing inflammation throughout the body.
Hair loss can occur due to inflammation of the scalp (discoid lupus) or as a result of the overall stress and illness caused by SLE.
The disease is fairly uncommon, affecting 28 in 100,000 people.
However, sadly, it has no cure, though treatment can ease symptoms over time.
But is there any way to treat lupus-related hair loss?
In this article, you will learn everything there is to know about lupus hair loss.
What is lupus?
Lupus is an autoimmune disease, causing the body’s immune system to attack certain organs and tissues.
As a result, inflammation can affect the skin, blood cells, kidneys, joints, and major bodily organs.
According to the Lupus Foundation of America, nearly 5 million people worldwide have a form of lupus, with approximately 16,000 new cases occurring every year.
90% of the people living with lupus are women, mainly between the ages of 15-44.
Common symptoms of lupus include:
- Stiffness and joint pain
- Skin rashes (particularly on the cheeks and/or nose)
- Tiredness which doesn’t ease regardless of how much you rest
- Sensitivity to light
- Swollen glands
- Weight loss (without obvious lifestyle causes)
It ranges in severity, from mild to severe.
People with mild cases are likely to experience skin and joint issues, as well as tiredness.
2 out of every 3 lupus patients, have similar symptoms to rheumatoid arthritis, where the immune system mainly goes after the joints.
Moderate cases lead to inflammation of the kidneys, lungs, heart, or other areas of the body.
And in severe cases, inflammation can cause serious damage to the lungs, brain, heart, or kidneys — posing a risk of death.
Symptoms may worsen and ease from time to time, or remain the same consistently.
Treatments for lupus include ibuprofen or other anti-inflammatories, as well as steroid injections, creams, or tablets.
Hydroxychloroquine may be prescribed for skin and/or joint problems, and fatigue.
Is hair loss a sign of Lupus?
Hair loss is a known symptom is lupus. However, if your only symptom is hair loss, it is unlikely that you’re suffering from the disease.
Hair loss can be a symptom of multiple health conditions, but if you suspect that you may have lupus it’s best to get a proper diagnosis from a doctor.
Why does lupus hair loss occur?
People with lupus won’t necessarily experience hair loss, but it can cause hair thinning or baldness in multiple ways:
1. Inflammation
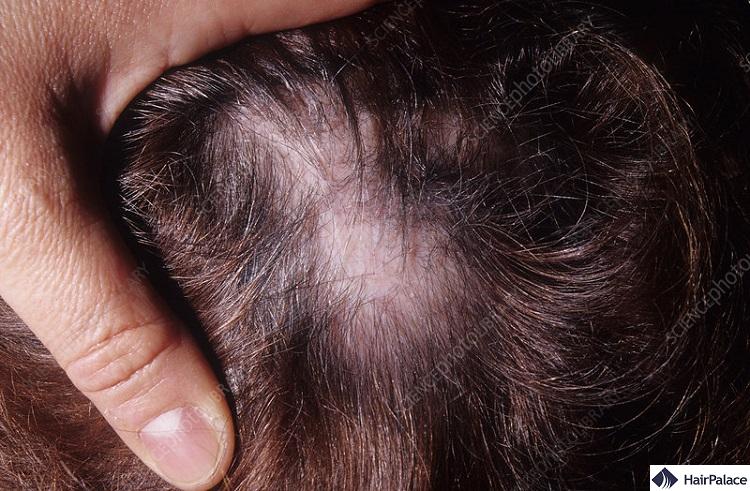
There are two types of lupus alopecia according to studies, scarring, and non-scarring.
Non-scarring hair loss usually happens as a result of inflammation.
Inflammation is a typical symptom of lupus, it is often widespread affecting several regions of the body.
When the inflammation affects the scalp and hair follicles, hair thinning may occur.
However, the inflammation caused by lupus is not always limited to the scalp.
It may affect your eyebrows, beard, eyelashes, and body hair.
Hair loss as a result of inflammation might be reversible, but only if the lupus is treated properly and the disease goes into a period of remission.
2. Subacute cutaneous lupus or discoid lupus sores/lesions
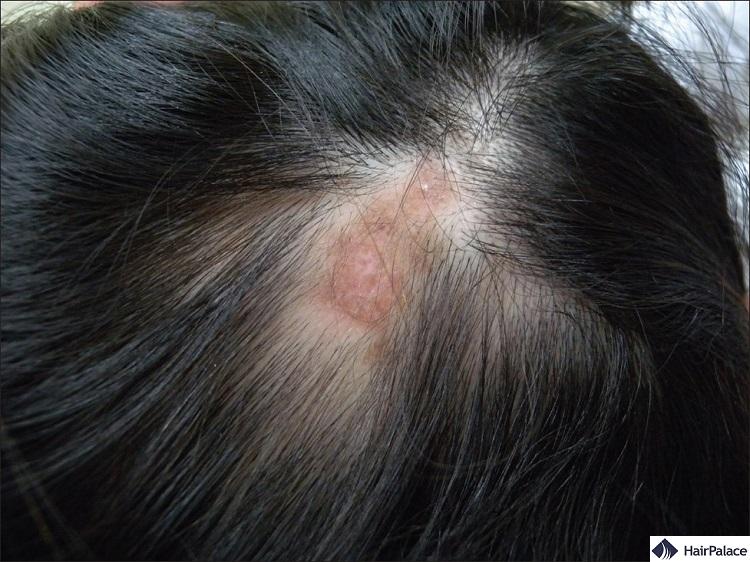
In certain cases, lupus can cause discoid sores or lesions.
These can take shape in the form of scalp lesions, but lesions and sores may appear anywhere on the body.
This can cause scarring and damage to the hair follicles, often resulting in permanent hair loss.
3. Medication
Many people with lupus experience hair loss due to the side effects of the medications used to treat the disease.
When hair loss happens due to medications the hair fall should stop once the treatment is discontinued.
However, it is important not to stop with any medication before seeking professional medical advice.
In certain cases where the hair loss is the result of a lupus flare-up, these medications might be actively helping to reduce the loss.
In case of severe illness, your doctor may prescribe an immunosuppressant.
These medications work by weakening your immune system and sending you into remission.
What are the symptoms of lupus hair loss?
There are two types of lupus alopecia according to studies, scarring, and non-scarring.
1. Scarring lupus hair loss symptoms
The first form of hair loss that can occur in people with lupus is referred to as “scarring alopecia”, this usually happens due to Discoid Lupus Erythematosus (DLE).
Its symptoms include:
- coin-shaped (discoid) lesions
- present on skin exposed to the sun, such as the head, neck or hand
- the lesions are typically red, scaly, and often raised which can lead to scarring
- most patients don’t develop Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE).
When these discoid lesions develop on the scalp they tend to cause permanent hair loss in the affected areas.
2. Non-scarring hair loss symptoms
People who are affected by Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) usually experience a form of non-scarring hair loss.
Non-scarring lupus hair loss in men is characterized by:
- gradual thinning on the scalp that is not necessarily permanent
- diffuse hair loss that is mainly limited to the frontal region of the hairline
- hair can appear more fragile, prone to breakage, and shorter than usual
- hair loss occurs due to the hair follicles being in a resting state during the periods when lupus disease activity is higher.
The reason this happens is likely due to the body attempting to save energy by focusing on more important bodily functions and ignoring non-essential functions such as hair regrowth.
This form of hair loss is referred to as Telogen Effluvium (TE), and it’s usually reversible as it doesn’t tend to damage hair follicles.
Another common non-scarring alopecia in people who have this autoimmune disease is called alopecia areata.
Alopecia areata is also an autoimmune disorder, the immune system attacks each hair follicle and causes patchy hair loss in small areas.
How can you treat lupus hair loss?
Lupus-related hair loss can be reversible as long as you have healthy tissue on the scalp.
However, hair loss will only reverse if the disease goes into remission.
Several drugs can be used to reduce lupus flares, including corticosteroids, immunosuppressants as well as antimalaria drugs.
Your doctor may administer biologics, which are intravenous drugs often used to alleviate lupus symptoms.
In some cases, it can take weeks or months of treatment before lupus goes into remission. In the meantime, here are some useful tips to help you deal with hair loss:
- Avoid sun exposure: UV light may trigger lupus flares and cause discoid lesions on the scalp. Always protect your skin when you’re outdoors. Either wear a hat or apply sunscreen to the exposed skin.
- Consider changing your medication: If you suspect that your medication might be contributing to hair loss, consult with your doctor to discuss alternative drugs, and perhaps reduce the dosage.
- Have a balanced diet: Incorporate fruits and vegetables into your diet as these may help you slow hair loss.
- Increase vitamins: Ask your doctor for recommendations about vitamins and supplements that can strengthen your hair. Some of the best vitamins for hair growth include biotin, vitamin C, vitamin D, iron, and zinc.
- Reduce stress: Some factors may trigger a lupus flare and make hair loss worse. Stress is one of the known triggers of lupus. To reduce stress, consider exercises and meditation.
- Get enough rest: Aim to sleep at least 7 hours a day
Natural remedies for lupus
Aside from managing lupus flares, here are a few tips that may help to keep your hair healthy:
- Have a balanced diet rich in protein, fats, and vitamins
- Exercise regularly to keep stress in check
- Try out stress reduction techniques such as yoga, meditation and breathing exercises
Vitamins and other mineral supplements can contribute to hair health.
Biotin is often recommended for people with hair loss. Although there is little evidence to suggest that it is actually effective.
Other essential nutrients for healthy hair growth include omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins A, B, C, and D, and minerals such as zinc, iron, copper, calcium, selenium, and magnesium.
Keep in mind that dietary supplements may interfere with certain medications, so it is a good idea to talk to a doctor before you decide to take any supplements.
Can hair transplants treat lupus hair loss?
Hair transplants may help people with hair loss due to autoimmune systemic diseases such as lupus.
A hair transplant is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that involves moving hair from one area of the scalp to another.
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE), the most popular hair transplant procedure, involves the removal of individual hair follicles usually from the back or sides of the head and translating the into the areas affected by baldness.
However, you should only consider a hair transplant if your lupus is under control.
Otherwise, the inflammation that caused the hair loss in the first place may jeopardize the success of the procedure.
Styling Lupus Hair
Choosing the right hairstyle may help you hide your lupus hair loss hairline.
Altering your part, cutting your hair shorter, or adding layers can give the appearance of fuller hair while also camouflaging bald spots.
You can also use wigs, scarves, or hair extensions to hide how much hair you lost.
You should keep in mind that not all forms of lupus-related hair loss are preventable.
To ensure that hair grows as it’s supposed to, you should be gentle with your hair.
Implementing a few useful hair care tips may reduce the number of broken hairs:
- Try to sleep on a satin pillow to prevent hair breakage
- Make sure that your hair is well moisturized. Dry and brittle hair can easily break off, resulting in fewer strands.
- Avoid colouring or overusing heat-styling products until your lupus is under control.
- Limit the use of brushes and tight rollers.
- Refrain from using heat-styling tools such as curling irons or straighteners.
- Consider letting your hair air dry instead of using a blow dryer.
- Avoid any chemical treatments as much as possible as they can damage hair roots and contribute to further hair loss.
When should you see a doctor?
You should always consult with a healthcare professional regarding any type of hair loss or thinning.
Your hair loss might be caused by a health condition other than lupus, or it can be a combination of multiple reasons.
Skin lesions and other lupus symptoms should be treated with the utmost care to avoid scarring and permanent hair loss.
Contact a rheumatologist immediately if you notice any lesions or rashes appearing on your scalp.
You should also contact a doctor if you are losing large clumps of hair or if you experience hair loss after starting a new medication.
People with lupus typically see their rheumatologist every three or four months.
If you notice minor or mild hair loss, you should tell your doctor at your next appointment.
Although hair loss can happen due to certain medications, it can also be a result of several conditions other than lupus.
Your doctor can send you for a blood test to find the root cause of your hair loss and administer the right treatment.
Lupus Hair Loss FAQ
System Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) most commonly causes non-scarring alopecia, which creates thinning hair. This primarily occurs at the front of the hairline, but hair loss may not always be permanent.
With lupus, hair loss may result from disk-shaped discoid lesions on the scalp (though they may form on the face too). These create permanent scars, which may appear scaly and red without causing discomfort.
Lupus-related hair loss can often be reversed if it’s due to the disease’s activity or medication. However, if scarring occurs, the hair loss may be permanent. Proper treatment and management of lupus are crucial for hair regrowth.
Treatment is done by managing the underlying lupus activity with appropriate medications, adjusting any hair loss-causing drugs, and using topical treatments like minoxidil.
Hair loss is a known symptom of lupus, but it can also be a sign of some other underlying health condition. It’s always best to get an accurate diagnosis before coming to any conclusion.
Lupus causes hair loss primarily due to inflammation of the scalp and hair follicles. This autoimmune response can damage the follicles, leading to hair thinning or patchy hair loss. Additionally, some medications used to treat lupus can also contribute to hair loss.
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and discoid lupus are the types of lupus that can cause hair loss.
Last medically reviewed on July 30th, 2024
- Pons-Estel GJ, Alarcón GS, Scofield L, Reinlib L, Cooper GS. Understanding the epidemiology and progression of systemic lupus erythematosus. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2010 Feb;39(4):257-68. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2008.10.007. Epub 2009 Jan 10. Review.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19136143
- Wallace, D.J., & Hahn, B.H. (2013). Dubois' lupus erythematosus and related syndromes. (8th ed.) Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders.
- Barber, M. and Clarke, A. (2017). Socioeconomic consequences of systemic lupus erythematosus. Current Opinion in Rheumatology, 29(5), pp.480-485.
- Carter, E., Barr, S., & Clarke, A. (2016). The global burden of SLE: prevalence, health disparities and socioeconomic impact. Nature Reviews Rheumatology, 12(10), 605-620. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2016.137
- Meacock, R., Dale, N., & Harrison, M. (2013). The Humanistic and Economic Burden of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Pharmacoeconomics, 31(1), 49-61. doi: 10.1007/s40273-012-0007-4
- Gong Y, et al. (2013). Severe diffuse non-scarring hair loss in systemic lupus erythematosus - Clinical and histopathological analysis of four cases. DOIhttps://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22176340
- Parodi A, et al. (2014). Hair loss in autoimmune systemic diseases.https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Emanuele_Cozzani/publication/260378310_Hair_loss_in_autoimmune_systemic_diseases/links/555c843208ae6aea08185eb5/Hair-loss-in-autoimmune-systemic-diseases.pdf


