Hair Types: How to Identify, Maintain and Style Yours
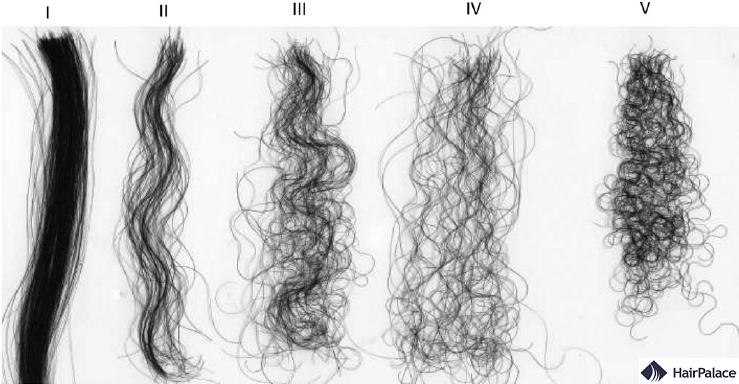
Do you know your own hair type?
And does it really matter if you don’t?
Understanding your own hair type is crucial to maintain good hair health, just as knowing your skin type helps you choose the best cosmetics and moisturizers.
If you don’t know what to do and what not to do with your hair, you could damage it severely over time.
But don’t worry: this quick, simple guide will help you identify your hair type — and take better care of it.
- What are the hair types?
- How to identify yours
- Type 1
- Type 2
- Type 3
- Type 4
- Hair care tips
- Hair porosity and density
- How to restore growth
What are the hair types?
Your hair type is based on your hair’s natural curl pattern.
The amount of curl in your hair is largely influenced by your hair follicles, as well as whether you have thick or fine hair.
You may have:
- straight hair
- wavy hair
- curly hair
- coily hair
People with curlier hair usually have more oval or asymmetrical hair follicles.
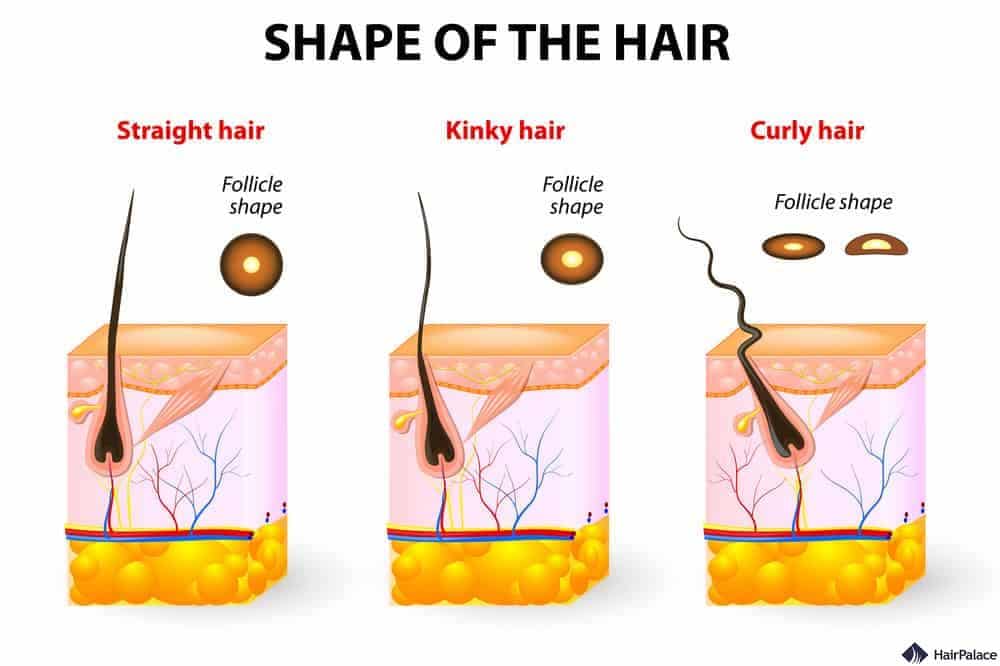
Genetics is the biggest contributing factor that determines the type of hair you have.
Notably, African hair tends to be more coiled and dry, while Asian hair is typically straighter and thicker.
Caucasian hair is somewhere in between with 45% having straight hair, 40% having wavy hair, and 15% having curly hair according to data provided by GB HealthWatch.
You may alter your curl patterns with certain hair care products that use heat or chemicals, and your curl pattern may change due to hormonal imbalances or as a side effect of certain medications.
However, your basic curl pattern is rooted in your DNA.
Every time your hair goes through its growth cycle, those genetic characteristics are reasserted.
Hair type chart
Your hair can be classified in several ways, but the Andre Walker system is the most popular.
Mr Walker is an award-winning hairstylist known for working on The Oprah Winfrey Show, and for styling many celebrities’ hair (including Oprah, Michelle Obama, and Halle Berry).
He developed the Andre Walker Hair Typing System to help market his hair care products.
The chart includes four main female, and male types of hair, with sub-categories in each.
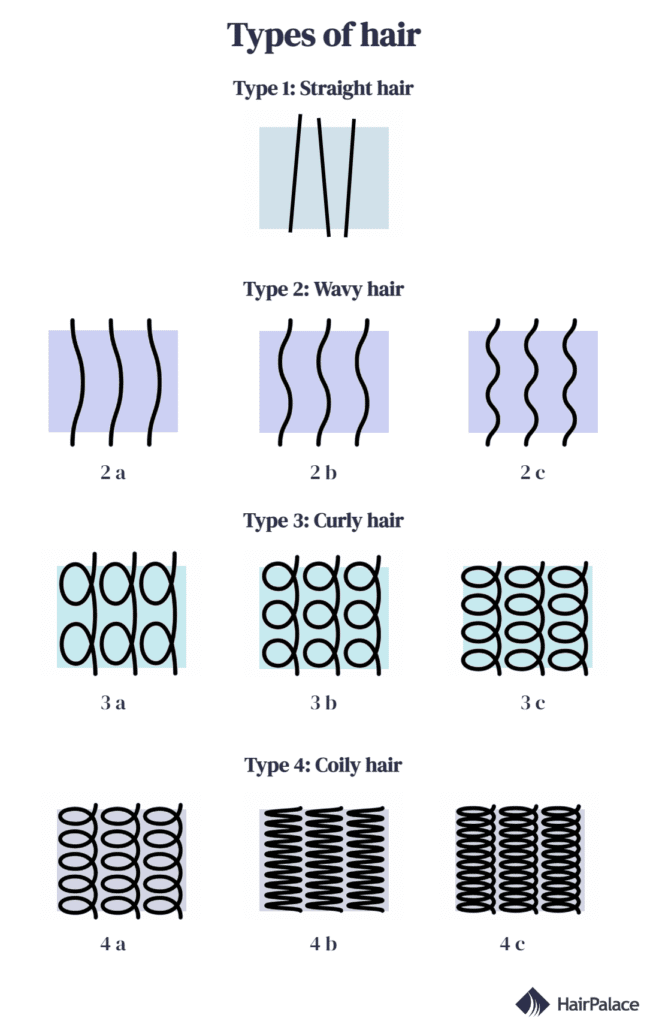
Type 1: Straight hair
Type 1 hair is completely straight; it has no wave or curl pattern.
The hair strands can be fine or coarse, and the hair may be thin or thick.
Straight hair is the strongest, which means it resists damage well but can be difficult to curl or add waves to.
However, it is also the oiliest type. Sebum can pass from the scalp to the hair ends easily when there are no kinks or curls, often resulting in oily hair.
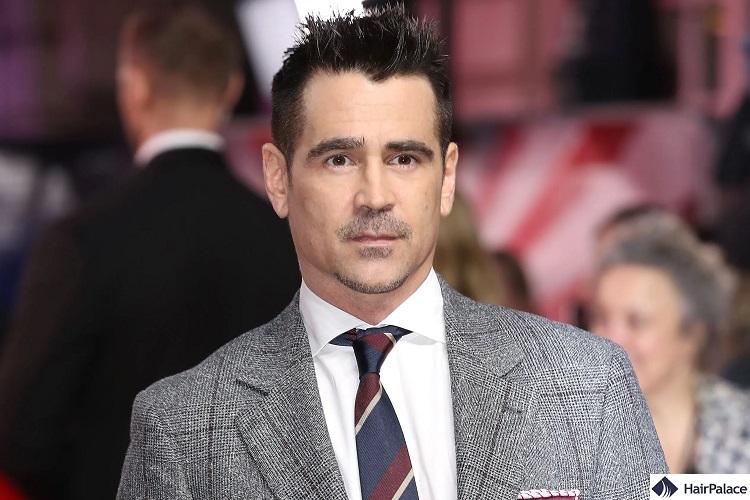

1A Hair type
Type 1A is as straight as straight hair can get. The hair rests flat on the scalp with this hair structure and there is no natural wave or curl pattern.
There is not as much volume, and you may find it challenging to style this hair into curly hairstyles.
The hair often has a gloss to it as this hair type can be oily.
1B Hair type
Type 1B is one of the most common types of hair.
This subcategory is defined by hair of medium thickness, which has more volume than type 1A. It may hold a curl and it’s not as flat or hard to style as type 1A.
1C Hair type
Type 1C is characterized by coarse, thick hair that has a light wave pattern. It still lies flat on the head, but it has extra hold which allows for easier creation of waves and curls.
The main downside of having 1C hair is that it is much more prone to frizz.
Type 2: Wavy hair
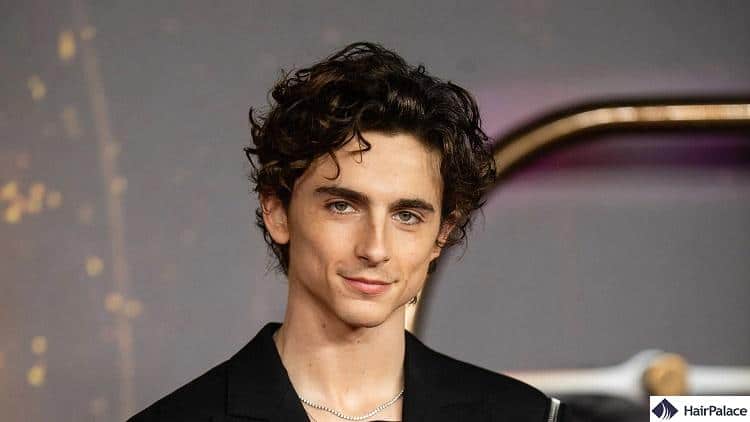

Wavy hair has a distinct S shape. This is one of the most coveted hair textures because it creates a gorgeous, tousled appearance, and it’s extremely easy to style.
This type of hair falls between straight and curly, though it may take on a frizzy appearance.
2A Hair type
Type 2A appears straighter than 2B or 2C, and it only has a mild wave pattern.
The hair follicle looks straight at the roots but develops a loose wave towards the ends.
2A also appears thinner and finer than other subcategories.
It is essential to find the right hair care products to maintain volume and highlight the slight wave.
This hair type works well with both straight and curly hairstyles.
2B Hair type
Type 2B is the second subcategory, which is distinguished by a more defined natural wave pattern.
The top of the hair appears straight, with the wave becoming more pronounced from the midpoint.
This hair structure is also prone to frizz. This is the best hair texture for beachy waves and softer hairstyles.
2C Hair type
Type 2C is characterized by luscious thick hair. Other than hair thickness, this type can also be easily identified by the strong waves that start straight from the roots.
The hair consists of distinct S shapes and can be prone to frizz in more humid climates. This hair texture looks best when the waves are well-defined.
Type 3: Curly hair
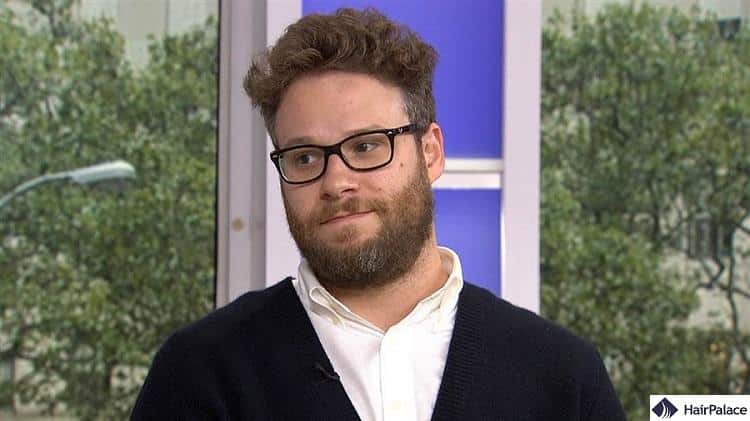

Curly hair has a visible S or Z shape with lots of volume. The appeal of curly hair is the ease of styling.
Type 3 hair floats around the head, which is flattering on all face shapes and provides a youthful appearance.
3A Hair type
Type 3A has loose curls which look less thick than other curly hair.
The hair may lay flatter on the scalp, and it’s also less prone to frizz. The curls can appear loopy, with a defined S shape.
It is important to be careful when you’re styling your hair in order to avoid damage to the hair shaft.
You should also avoid hairstyles that pull at the scalp or hairline, such as buns or ponytails.
3B Hair type
Type 3B is characterized by springy ringlets, and it has a thicker appearance than 3A, with the curls being wider and tighter.
3B is also prone to frizz, and you may find it a bit more challenging to style.
This hair texture doesn’t lie flat on the scalp, and it’s less likely to become oily. Proper hydration is essential for this hair type, as it has a tendency to be prone to dryness.
You should use a gentle shampoo that provides hydration and extra moisture.
Additionally, you should avoid heat styling, as well as any hair care products that contain silicone or sulfates.
3C Hair type
The thick, tight curls spring from the roots with type 3C. It has a stunning texture, with the hair appearing voluminous and flexible.
However, type 3c can be prone to frizz and dryness, and requires a lot of care.
You should make sure to keep the hair’s natural moisture intact, with the help of shampoos or essential oils.
Just like with type 3B, avoid sulfates and silicones, as well as heat styling in order to maintain healthy hair.
Type 4: Kinky hair
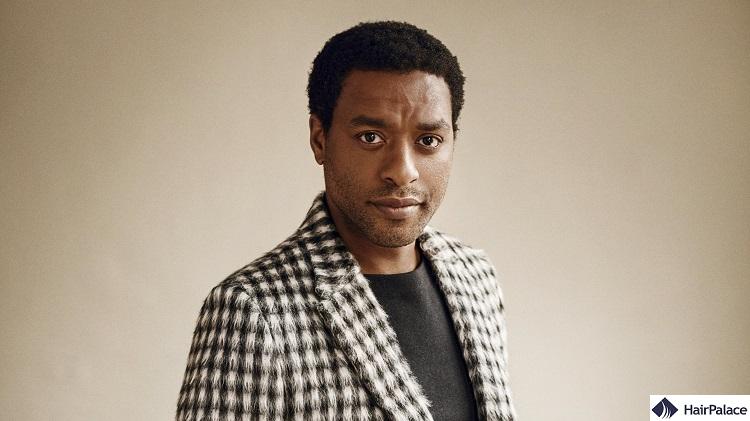

Kinky, or coily hair is usually thick but prone to damage.
That’s because kinky hair often shrinks when wet, as it has fewer cuticle layers than the other types of hair covered above.
The hair texture looks thick and full, but it has to be styled with great care.
This hair type requires a lot of moisture, and it’s very susceptible to outside damage, especially when the hair fibers are dry.
The texture of the curls may vary across the scalp. It might look coarse but is actually made up of many fine strands packed closely together.
4A Hair type
Type 4a is distinguished by tight coils that appear springy and full of movement.
4a hair usually retains its curls whether it’s wet or dry.
You need to care for this hair type with conditioning treatments to ensure it’s always well moisturized. Lastly, it’s important to avoid heat styling and tight hairstyles.
4B Hair type
Type 4B has a distinct Z pattern, which is less defined than the curl patterns of 4A hair.
The curls are tight, with the strands varying in thickness from coarse to fine.
You can try to use a curling cream to achieve a more defined pattern.
Just like with type 4A, you need to make sure your hair stays moist to maintain a healthy head of hair.
Furthermore, you should also avoid heat styling, as it may damage your strands and hinder hair growth.
4C Hair type
The last coily hair type is type 4C, which has the tightest curls. The hair is coarse and usually prone to shrinkage.
People with this type of hair have to be very selective when it comes to hair products, as improper hair care can easily result in hair breakages.
The 4C hair type in men is also vulnerable to dryness and damage, so you should make sure your hair is always well moisturized.
Leave-in conditioners, hair masks, or coconut oil can achieve this.
Hair care tips by type
Straight hair
- Remove knots from wet straight hair with a wide-toothed comb or your fingers, as a brush can cause it to break
- Avoid using too much product, which can weigh straight hair down
- Straight hair is prone to split ends, so trim it regularly (at least every six weeks)
- Only use gentle shampoos
- Dry your hair with a towel instead of a blow dryer
Avoid using the following hair products:
- Products for dry hair
- Natural oils such as olive or jojoba oil
- Leave-in products
- Oil-based styling products
Wavy hair
- Keep styling tools on a low heat to bring out the best in your waves
- Choose shampoos and conditioners which moisturise your hair to maximise waves
- Define your waves with your fingers, rather than a brush or comb (which can pull the waves out of shape)
Curly hair
- Avoid washing it daily — curly hair should be conditioned more regularly than it’s shampooed
- Wash your hair with cold water to reduce the risk of frizzing and to add shine to thick curls
- Detangle your hair with a wide-tooth comb carefully, one section at a time, to avoid putting too much strain on tight curls
Kinky hair
- Use moisture-rich hair loss shampoos, conditioners, and oils — this hair texture is the most brittle type
- Avoid products containing silicones, as they can be particularly harmful
- Don’t overdo protective styles: take breaks and let your hair free from time to time
- Don’t wash your hair more than once a week
- Use a conditioner at every wash
- Avoid braids, cornrows, or weaves as well as other tight hairstyles.
How porosity and density affect your hair
Hair Porosity
When hair stylists talk about your hair’s porosity, they mean your hair’s ability to absorb water.
If your hair has high porosity, that means it has a lot of holes in its surface layer, called the cuticle.
You may have high hair porosity by default, or your hair may have become more porous due to chemical and heat processing than it normally would be.
The holes in the cuticle allow your hair to soak up extra moisture which can result in frizzy hair, especially in more humid climates. This is because the cuticle is drawing moisture from the air.
The beneficial side of this is that high hair porosity also allows you to absorb moisturizing products better.
Rich creams, butters to leave-in conditioners can help make your hair more manageable, as these products seal the cuticle.
Hair with low porosity is tightly locked, and resists moisture better, whether it comes from environmental humidity or chemical processing.
In order to avoid product build-up which can weigh down and dull your hair, consider washing with a clarifying shampoo on a weekly basis and opt for lighter hair care products to create volume.
Heat styling your hair might be beneficial if you have low porosity, as the heat can open up the tight cuticle and allow your hair to soak up moisture.
Hair Density
Hair density depends on how many hairs you have on your head. On average we have 100,000 hairs on our scalp, but it varies from person to person.
In general, if your scalp doesn’t show through, you have high hair density.
However, if your scalp shows through without parting your hair, you are likely to have thin hair.
The density of your hair can be affected by a number of factors, such as hormones, stress, menopause, nutrition or even the products you apply regularly.
Thin, low-density hair can easily get weighed down by products, so a light mousse or a texturizing spray are better options to add more volume to your hair.
If you have high-density, thick hair, you may need rich creams for more shine and control.
Restoring growth for all types of hair
Understanding the different types of hair and following our tips can help you take better care of your locks.
But regardless of your hair type, you may experience hair loss due to genetics, hormonal changes, stress, and various other factors.
And there are multiple treatments available:
- Best vitamins for hair
- Hair growth products
- Scalp massage
- Hair tattoo
- Laser theraphy
- PRP hair treatment
If you want to restore your thinning hair permanently, with natural, thicker growth, hair transplant surgery can help.
Speak to a member of our team to learn more about how you can save up to 70% on your hair transplantation cost.
Hair Types FAQ
There are four types: straight, wavy, curly, tight curls.
Everyone has a unique hair texture. A number of factors (primarily genetics) determine the type and texture of your hair, and straight hair is one of the most common types.
Hold one of your hairs and examine it closely.
Thin: If you can barely feel the hair in your hand, your hair is thin.
Medium: If you can feel the hair between your fingers slightly, your hair is of a medium thickness.
Thick: If you can clearly feel the hair, your hair is thick.
Yes, white people can have type 4 hair. While type 4 hair is mainly seen in African American women and men, this curl pattern is not race-specific. People of all ethnicities, including Caucasians, can have type 4 hair, although it is highly uncommon.
Any of the 12 types listed above are not limited to a specific race or ethnicity and can be found in anyone. While it is certainly rare to see a white person with coily or kinky type 4 curls, it is far from impossible.
Type 5 hair is usually used in reference to hair composed of curly and frizzy textures with fine shafts. Type 5 hair can vary from coiled tightly or loosely, and its curls take on an S or Z shape that could be classed as 3A to 4C type hair.
To determine it, consider these factors:
–Texture: Is your hair straight, wavy, curly, or coily?
–Porosity: Does your hair absorb moisture easily or does it repel water?
–Density: Do you have a lot of hair strands or is it sparse?
–Diameter: Are your hair strands fine, medium, or thick?
Comparing these characteristics with charts available online can help you identify your specific hair type.
To identify your type of curly hair, consider these categories:
Wavy (Type 2): S-shaped waves; ranges from 2A (loose waves) to 2C (more defined waves).
Curly (Type 3): Defined, springy curls; ranges from 3A (loose curls) to 3C (tighter curls).
Coily (Type 4): Tight coils; ranges from 4A (soft coils) to 4C (very tight, almost zig-zag pattern).
Examine your hair’s curl pattern and compare it to these types to determine your specific type.
Type 4 hair is known for its tight coils and kinks. It’s often characterized by its dense, fine texture and is divided into three subcategories:
–4A: Soft, defined coils with an “S” pattern.
–4B: Less defined pattern with a “Z” shape, more cotton-like feel.
–4C: Tightly coiled with a more zig-zag pattern, often experiences the most shrinkage.
Asian hair is typically straight, thick, and dense, with a round or slightly oval hair shaft, making it resistant to curling.
You can’t permanently change your natural hair type, but styling, treatments, and chemical processes (e.g., perming, relaxing, or keratin treatments) can temporarily alter its texture
Last medically reviewed on February 18th, 2025
- Healthline on beauty and skin carehttps://www.healthline.com/health/beauty-skin-care/types-of-hair
- The Trend Spotter on hair typeshttps://www.thetrendspotter.net/hair-types/
- Curlcentric on hair types https://www.curlcentric.com/can-white-people-have-type-4-hair/#:~:text=White%20people%20can%20have%20type,hair%2C%20although%20it's%20not%20common.


