Rogaine for Hair Loss: Does it Work?

Rogaine is one of the most popular medications for treating hair loss, which is clinically proven to help regrow hair for both men and women.
It’s also incredibly straightforward to use!
It works by stimulating hair follicles, increasing blood flow to the scalp, and prolonging the hair growth phase.
The result? Stronger, healthier-looking hair that stays on your scalp for longer.
Rogaine has so much potential; you must know all the facts to make an informed decision on your haircare.
Our in-depth article will help you find all the answers to your questions.
- How it works
- For men
- For women
- Before and after
- Side effects
- How to use
- Alternatives
- Products & prices
- Conclusion
What is Rogaine?
Rogaine is a vasodilator medication, which essentially means it opens blood vessels up, improving circulation.
When applied on the scalp, an increased blood flow ensures hair follicles receive all the nourishment required to sustain hair regrowth.
Its active ingredient is minoxidil. It’s thought that it increases the size of the hair follicle and extends the growth phase of hair strands during the hair growth cycle.
For these two reasons, Rogaine is often the perfect package to reverse hereditary hair loss.
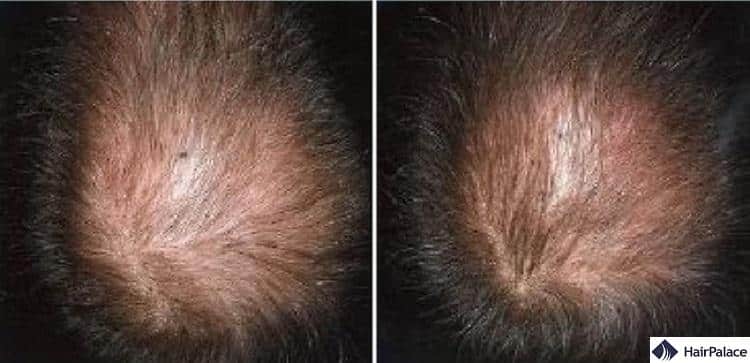
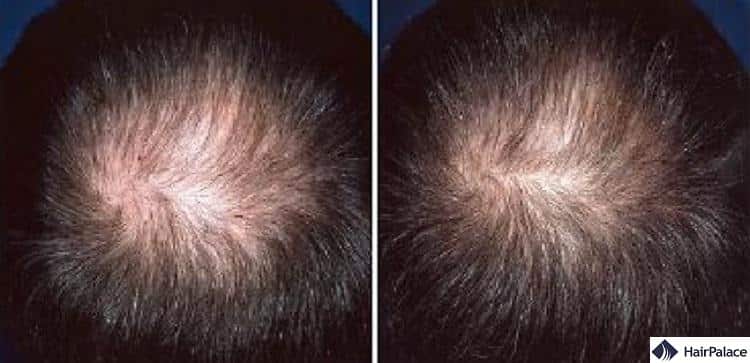
Rogaine for men
Research has shown that Rogaine can be an effective way to stimulate new hair growth in men suffering from hereditary hair loss.
A 2002 study showed that patients who used a 5% topical minoxidil reported clinically visible results; fuller hair, less hair shedding, and an overall increased hair count over the course of 48 weeks.

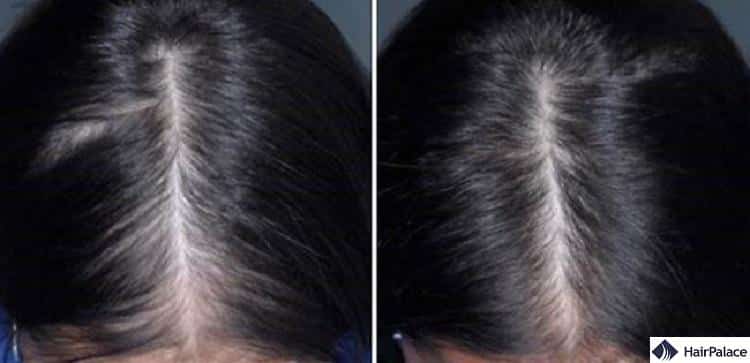
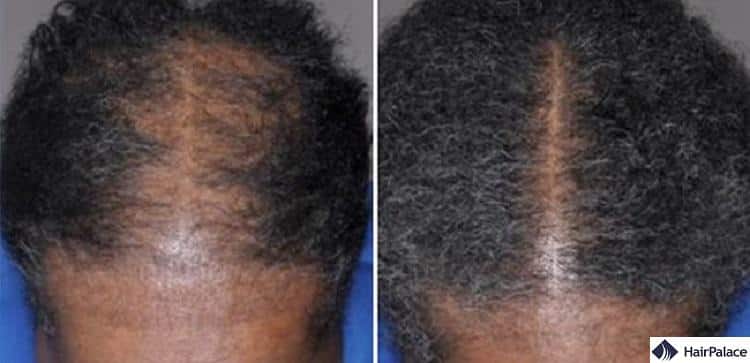
Rogaine for women
It can also promote hair regrowth for women, too.
Two studies examined the effects of a 5% and 2% solution of minoxidil on hair and found they lead to fuller appearances in women suffering from female pattern hair loss.
That said, the treatment is not recommended for pregnant or breastfeeding women.

Rogaine before and after
How long does minoxidil take to work? (Rogaine)
Generally, it takes about eight weeks of consistent use for patients to notice any results.
At four months, hair loss should have stopped, with new hair growth developing.
When patients start a course of this treatment, they might become alarmed that they are losing more hair than usual. Don’t be alarmed – this is to be expected.
The active ingredient minoxidil speeds up the resting phase of the hair follicle. But minoxidil also extends the growth phase, leading to stronger, longer, thicker hair regrowth.
Who will see the most impressive results?
As with any cosmetic treatment, appearances do matter. No doubt you’re interested in who responds well to this medication.
Firstly, let’s talk about the condition and state of hair loss.
Rogaine is an effective way to reverse hereditary hair loss, especially in specific areas at the back of the head and around the scalp vertex.
It can also be effective in treating hair thinning in women. Finally, Rogaine is most effective for people aged 40 and under.
The closer you start treatment to when symptoms first appear, the better. If you’ve already lost all of your hair, it will not help you.
Who should avoid Rogaine?
As effective as this treatment can be, there are, of course, certain people who should not take it.
These include people who may exhibit the following:
- Your scalp is itchy, inflamed, overly sensitive, or discoloured.
- You’ve had an allergic reaction to minoxidil
- You’re experiencing sudden, patchy hair loss
- Your hair loss was a result of chemical products, treatments, excessive styling, or physical trauma
- Your hair loss results from alopecia areata (spot baldness), a hormone disorder, scarring, medication, or nutritional deficiency.
- You’re younger than 18 years of age
- If there’s no history of hereditary hair loss in your family
If in doubt, seek advice from your doctor, as they may recommend you try alternative hair loss treatments.
Rogaine side effects
Rogaine is a safe, clinically proven medication for hair loss.
Any potential side effects are considered low-risk and very easy to manage. They include:
- Irritation of the scalp
- Unwanted facial hair growth
- Changes in hair colour and texture
- Hair growth in unusual places like the forehead
You may shed more hair when you start a course of treatment – do not panic.
This is perfectly normal, as affected follicles begin to push out older hair. This process clears space for brand new hair strands to grow.
Though rare, some people may have a more severe reaction to the medication. Seek medical attention if you develop a medical problem such as:
- Feeling dizzy or faint
- Develop an irregular heartbeat or heart disease
- Start to feel chest pain
- Lose weight with no explanation
- If feet or hands begin to swell
If the solution accidentally comes in contact with your eyes, you must rinse them immediately with cool tap water.

How to use Rogaine products?
Rogaine is a very straightforward hair loss medication to apply. But to get the most out of your treatment, consider the following tips:
- Always refer to the patient information leaflet supplied and follow its guidelines carefully. The average dosage is half capful two times per day.
- Only apply the solution to a dry scalp. About half a capful is the standard amount to use per session.
- Allow the appropriate time for the foam to dry before you style your hair
Can I touch my hair after using Rogaine?
After you apply the solution, you must allow it to dry for at least 4 hours. Don’t wash, blow dry or cover your head during that time.
Because minoxidil is a medication known to stain clothing, it’s recommended you time your treatment at such a time that you avoid touching clothing, bed linens, towels, and other fabrics.
Do you have to wash your hair everyday when using Rogaine?
Once the solution has dried, you should wash your hair.
If the medication stays on your scalp for too long, it may trigger unpleasant side effects, including scalp irritation, a burning sensation, or redness.
While you don’t have to wash your hair beforehand, your scalp must be dry and clean before application.
Can you sleep with Rogaine in your hair?
Yes, you can sleep as you usually would. That said, ensure the treatment has been washed off, as it can stain linens on contact.
What happens when your stop Rogaine?
Sadly, it is not a permanent solution for hair loss. If you stop, regrown hair will begin to fall out within 3 to 4 months. Only by continuing treatment will results stay.
Alternatives to Rogaine
Currently, there are only two FDA-approved medications to treat androgenetic alopecia; Finasteride and Minoxidil.
Best Rogaine alternative: Finasteride (Propecia)
Finasteride can be an effective medication to combat hair loss. It works by blocking a hormone known as dihydrotestosterone (DHT), which shrinks follicles to such a degree that they cannot grow new hair.
Finasteride prevents testosterone from converting into DHT, dramatically reducing its presence in your body and subsequently preventing hair loss.
Finasteride is available in pill and topical form, though the pill version is much more commonly used.
Despite their differences, both finasteride and minoxidil can be effective treatments.
Minoxidil
Minoxidil is clinically proven to increase blood flow to your scalp.
This, in turn, provides more nourishment and support to your hair follicles, which produce stronger, healthier new hair.
Minoxidil is the active ingredient in Rogaine, though other hair growth products are similarly designed to achieve equally impressive results.
Minoxidil 10% may be beneficial for those who gained lacklustre results from the 5% solution.
The only thing that distinguishes Rogaine from other drugs is the inactive ingredients that may be used in production.
Minoxidil can be especially useful when used in combination with a derma roller.
These devices can increase your scalps’ ability to absorb minoxidil, leading to better overall results.

Rogaine price
Like any cosmetic medication, the price can vary depending on the type of treatment (foam, solution, etc.) and the store you buy it from.
For example, on Amazon, let’s take a quick look at two of the most popular products and their prices, the extra strength scalp foam and solution.
- A 3-month prescription of Rogaine Men Extra Strength scalp foam costs around £68.
- A 3-month supply of Rogaine Men Extra Strength scalp solution costs £63.
| Product | Price | Size | Amazon reviews |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rogaine for Men foam | £ 22.90 | 73ml | 4.2 based on 6702 Amazon reviews |
| Rogaine for Men solution | £ 23.90 | 60ml | 4.0 based on 1981 Amazon reviews |
| Rogaine for Women foam | £ 24.50 | 73ml | 4.2 based on 2217 Amazon reviews |
| Rogaine for Women solution | £ 24.90 | 60ml | 3.9 based on 1448 Amazon reviews |
When should you seek medical help?
Hair loss in and of itself can be challenging to face. And it can be a sign of an underlying condition.
You should consult with your doctor and get their advice on treatments. If you show the following symptoms:
- A receding hairline
- Thinning hair
- Your hair part is widening
- Bald spots increase in size
- Losing hair from around your body, including facial and chest hair.
Although Rogaine hair loss treatment is proven to regrow hair, it is not the only solution for you, as several other products can still prove more effective.
Visiting your doctor for a proper diagnosis is therefore essential.
Patients using this medicine should see results within six months of continued use.
You should refer your doctor for alternative therapies if you do not see any changes.
It also has some side effects that you must be aware of when using.
If you begin to suffer from these, stop using the product and visit your doctor immediately.
Minor side-effects include scalp irritation, burning, itchiness, or redness, to more extreme side-effects like chest pain, irregular heart rate, or hand and foot swelling.
Conclusion
Rogaine can be an effective treatment for hereditary hair loss, such as male pattern baldness, and has gained the support of many doctors and haircare professionals.
However, its efficacy is not guaranteed for everyone, and it requires continuous use to maintain hair growth, which can become costly over time.
Additionally, the long-term side effects of Rogaine are not well-known, and stopping the treatment will result in hair loss.
In contrast, a hair transplant offers a permanent solution, with procedures like the innovative FUE hair transplant boasting a success rate of 90-95%.
This method provides a natural-looking restoration suitable for various hair types and forms of hair loss.
FAQ
Men’s Rogaine (minoxidil) is generally effective for treating male pattern baldness in many individuals.
For best results with Rogaine, apply it twice daily to a dry scalp, use the recommended amount, and ensure consistent, regular use as directed.
Initially, Rogaine may cause temporary hair shedding, but this is typically a sign of new hair growth cycle beginning. It’s not long-term hair loss.
Rogaine typically takes about 3 to 6 months to show visible results.
Rogaine can work on bald spots caused by conditions like androgenetic alopecia or telogen effluvium, as it stimulates hair follicles and promotes regrowth. However, it is less effective on long-standing, completely bald areas where follicles are no longer active.
Yes, you can use Rogaine after a hair transplant, as it may help improve overall hair density and support the growth of transplanted and existing hair. However, consult your surgeon for the right timing and guidance, as its use is typically started a few weeks post-surgery.
Rogaine (minoxidil) is not FDA-approved for receding hairlines, but it may help some individuals regrow hair in that area. Results vary, and it is generally more effective on the crown than the hairline.
Rogaine doesn’t stop working at a specific age but becomes less effective if hair follicles are no longer active or if hair loss progresses significantly over time. Consistent use is key, regardless of age, to maintain results.
Last medically reviewed on January 16th, 2025
- Suchonwanit P, Thammarucha S, Leerunyakul K. Minoxidil and its use in hair disorders: a review. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019 Aug 9;13:2777-2786.https://doi.org/10.2147%2FDDDT.S214907
- Olsen EA, Weiner MS, Delong ER, Pinnell SR. Topical minoxidil in early male pattern baldness. Journal of Am Ac Derm. 1985;13(2):185-192https://doi.org/10.1016/S0190-9622(85)70157-0
- Messender AG, Rundegren J. Minoxidil: mechanisms of action on hair growth. British Journal of Dermatology. 2004150(2):186-194.https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2133.2004.05785.x
- Shapiro J. Safety of Topical Minoxidil Solution: A One-Year, Prospective, Observational Study. Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery. 2003;7: 322-329.https://doi.org/10.1007/s10227-002-0121-6
- Rogaine label. (2006).https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2006/021812s000LBL.pdf
- Olsen EA, Dunlap FE, Funicella T, Koperski JA, Swinehart JM, Tschen EH, Trancik RJ. A randomized clinical trial of 5% topical minoxidil versus 2% topical minoxidil and placebo in the treatment of androgenetic alopecia in men. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002 Sep;47(3):377-85.https://doi.org/10.1067/mjd.2002.124088