Diffuse Thinning: Signs, Causes, & Treatment Options in 2025
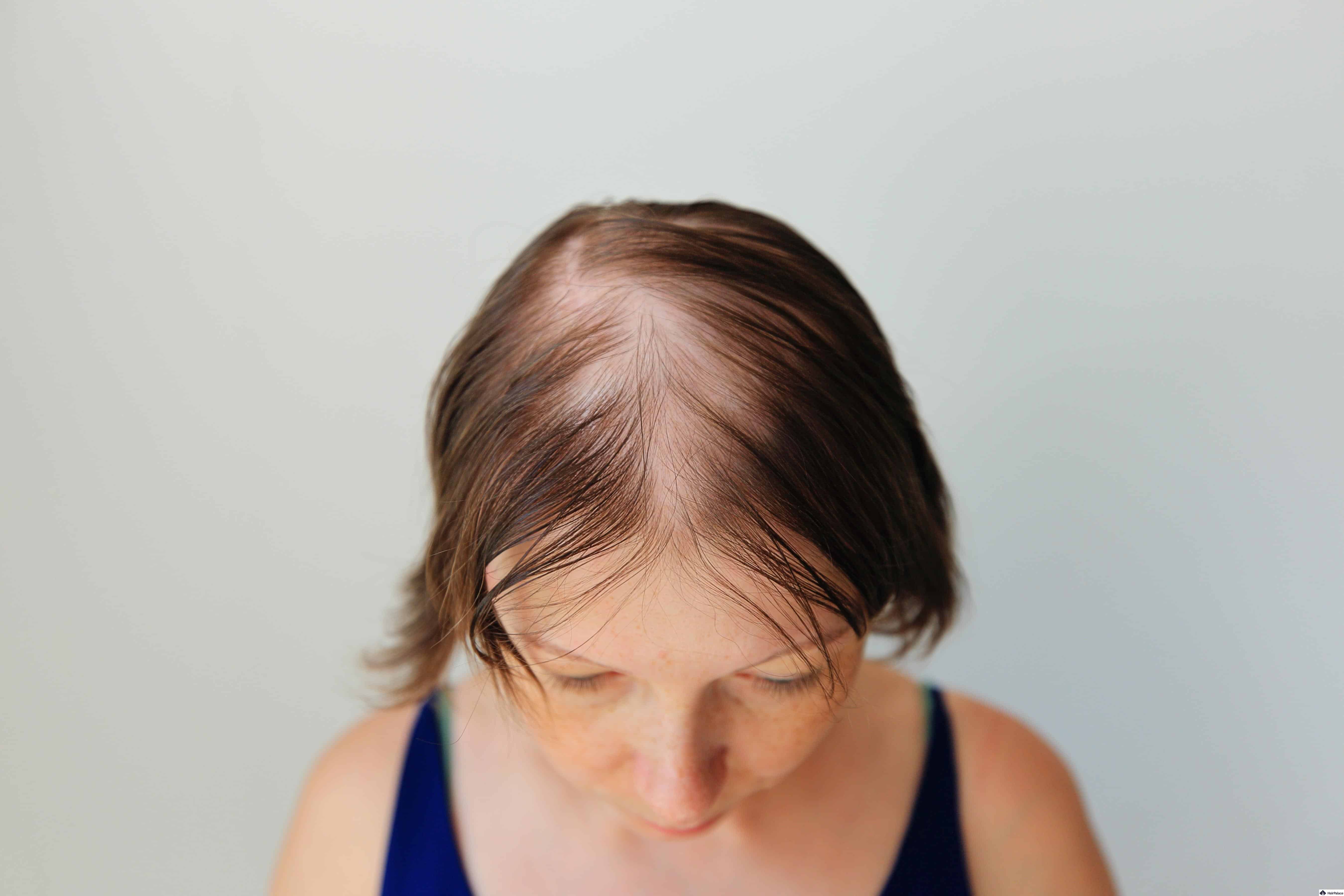

Whether it affects a small part or your entire scalp, diffuse thinning can be a very stressful and emotional thing to experience.
Diffuse hair loss is where hair thins uniformly across the scalp rather than in localized patches.
Various factors, including hormonal changes, nutritional deficiencies, stress, and underlying medical conditions such as thyroid disorders or telogen effluvium can cause this condition.
Treatment typically involves addressing the underlying cause, including nutritional supplements, stress management, and medications.
This article will highlight the most common causes of the condition and how you can get a formal diagnosis.
We’ll also explore a range of treatments known to help treat and potentially reverse thinning hair.
What is diffuse thinning?
Diffuse hair thinning male hair loss is defined by excessive hair shedding.
Strands become noticeably thin-looking; over time, hair becomes “see-through,” and your scalp is easily visible.
This condition is also known as diffuse unpatterned alopecia; as that name suggests, the condition does not follow an exact pattern.
Diffuse hair loss can be unpredictable, affecting only part of your hair in some cases, while in others, the entire scalp.
Additionally, it can affect both men and women, irrespective of their age.
Common causes of diffuse thinning hair include stress, medication, and hormone imbalances.
Genetic conditions like male and female pattern hair loss can trigger it.
Thankfully, various treatments are available that can help address and correct the problem, including simple lifestyle changes, medications, and in extreme cases, surgical procedures.
What causes diffuse thinning?
Diffuse thinning hair can occur at any age and may result from various factors, including an underlying health condition, medication, lifestyle choices, or stress.
Below, we’ll explore nine potential causes of diffuse thinning hair in men:
1. Hormonal imbalances
Hormones are vital in regulating several bodily functions such as hair growth.
Unsurprisingly, when hormone levels are imbalanced, your hair can suffer in various ways, including diffuse thinning.
2. Medications and medical treatments
Certain medications and medical treatments can aggravate male diffuse thinning.
Others may stunt the growth of hair completely.
This is especially true if treatment revolves around hormones, such as antidepressants or regulating blood pressure.
Furthermore, treatments like chemotherapy or radiation therapy can also cause dramatic hair loss, as healthy cells in the body, including hair follicles, are affected.
3. Alopecia Areata
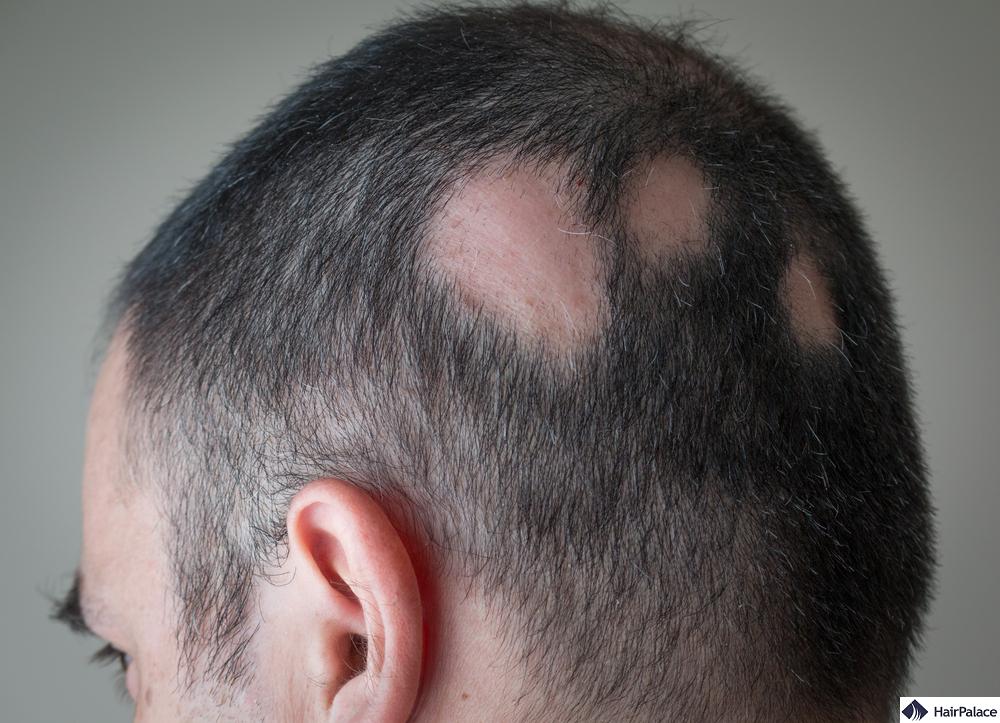
Diffuse alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition that sees your immune system attack hair follicles.
It can lead to hair loss and bald spots across your scalp and other body parts.
In severe cases, diffuse alopecia areata may lead to hair thinning across the entire body and complete baldness.
4. Telogen effluvium
Telogen effluvium is a hair loss condition that usually follows severe stress or a significant change in the body, e.g., surgery, illness, or dramatic weight loss.
More hair enters the resting phase of the hair growth cycle, leading to a thinning appearance across your scalp.
5. Thyroid disease
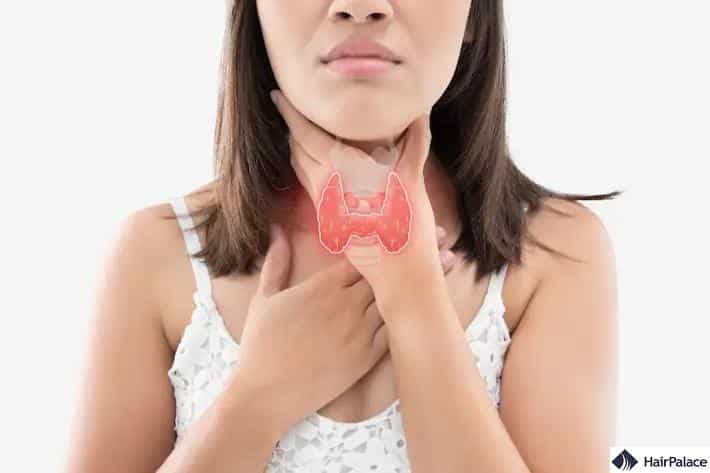
Your thyroid is an essential gland located near your windpipe.
It produces hormones that regulate everything from your heart and muscles to digestion and brain development.
An overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism) and an underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism) can contribute to diffuse hair loss.
6. Anagen effluvium
Anagen effluvium is when hair falls out during the active growing phase (anagen) of its hair growth cycle.
Extreme trauma and high-toxicity medications and treatments like chemotherapy usually trigger this condition.
7. Iron deficiency
Iron helps your body produce red blood and regulate a variety of hormones. As such, it is a building block for a healthy body and healthy hair.
If you are deficient in iron, you may experience various health problems, including diffuse thinning.
Try to eat more red meat, nuts like pumpkin and hemp seeds, and dark, green leafy vegetables like spinach or kale.
8. Anemia
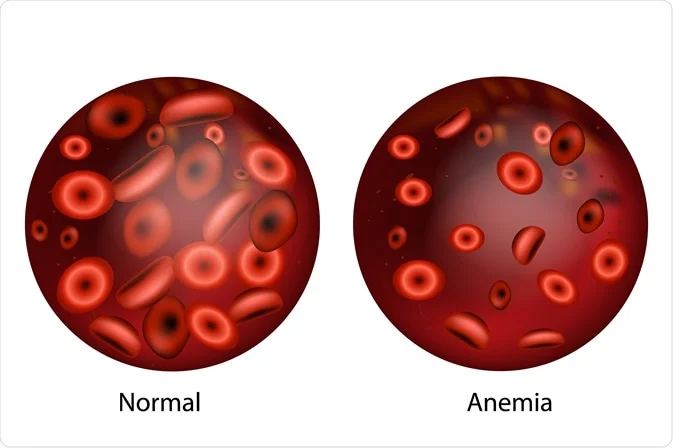
Anemia is when your body lacks the appropriate amount of red blood cells, thus reducing the amount of oxygen that can reach cells.
A lack of oxygen in scalp cells can result in early hair shedding.
Iron or B vitamin deficiencies, chronic illness, or inflammation can cause anemia.
9. Extreme stress
Finally, stress can be a leading cause of many conditions, including diffuse hair loss.
This is because, during stressful periods, your body will produce cortisol, a hormone that heightens our response to danger.
However, too much of this hormone can inhibit a hair follicle from growing new strands.
What are the symptoms of diffuse thinning?
Did you know that a certain amount of hair loss is perfectly normal?
We lose between 50-100 hairs each day. Under normal circumstances, our body can easily replace these hairs.
But what if hair loss seems unusually higher, and you’re beginning to see noticeable thinning and baldness developing? Should you be concerned?
Diffuse thinning progression can vary from person to person; it may happen suddenly or gradually over a more extended period.
It can take shape in diffuse thinning crown hair loss but it can affect any part of your body.
There are three core diffuse thinning symptoms you should be mindful of:
- Visible hair thinning across your scalp
- Excessive hair loss
- The scalp becomes easy to see, especially at the hairline, crown, and mid-region
How do doctors diagnose diffuse thinning?
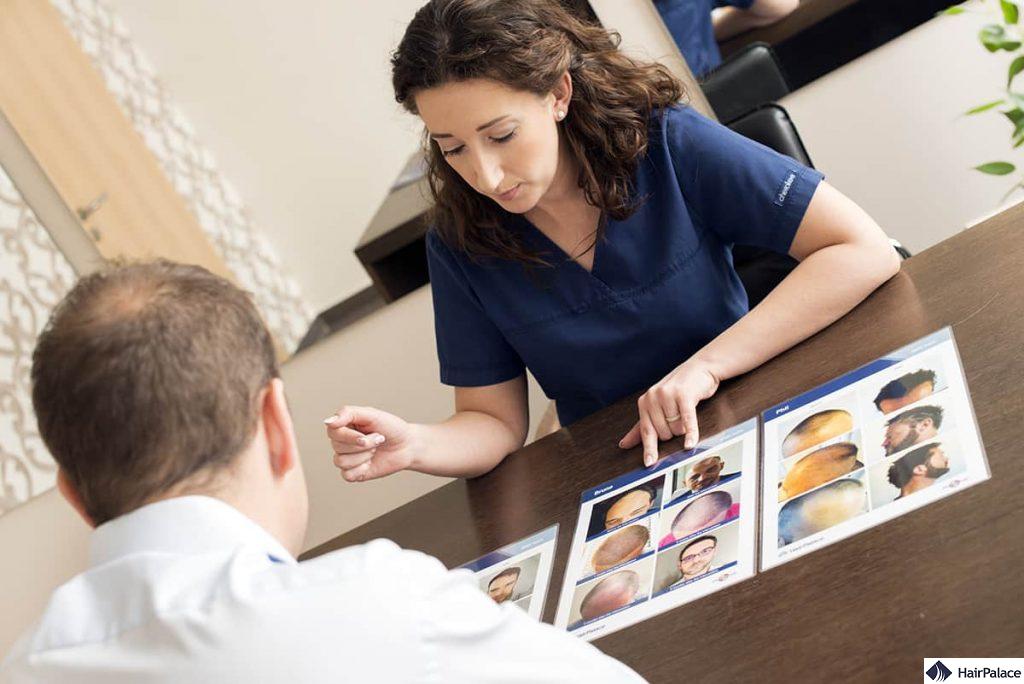

Doctors will use various methods to establish whether you’re suffering from diffuse thinning hair and the possible underlying causes.
These may include simple blood tests and examining your medical history.
They may also perform a hair pull test to see your hair’s strength and resilience.
8 options to treat diffuse thinning
Because every patient is unique, there are various ways to treat diffuse hair loss. What might work for one person may not work for you.
With that in mind, you should explore the following diffuse thinning treatment options:
- Underlying health conditions: These can include stress and anxiety disorders to autoimmune diseases like lupus and alopecia areata. Certain medications may also have the unwanted side effect of diffuse balding.
- Minoxidil: Commonly sold under the brand name Rogaine, this topical treatment is FDA-approved and can be bought over the counter for men and women.
- Finasteride: This prescription drug lowers the levels of DHT in your system, and thus slows down or even prevents further loss.
- PRP: This is an innovative treatment that can address a range of hair loss conditions, from common androgenetic alopecia to rarer forms of alopecia areata incognita and more.
- Low-level laser therapy: It works through a device known as a laser comb, which omits rays of light energy that stimulate cell growth and can also help reduce scalp inflammation.
- Hair growth shampoos: They can help clean your scalp and reduce inflammation, thus creating the ideal conditions for hair growth.
- Hair loss supplements: Our body requires essential minerals and vitamins to function correctly, supplements aim to replenish our stores and, in turn, stimulate follicles to grow.
- Lifestyle changes: Easy lifestyle changes can yield significant results for your hair. For example, eating a balanced, healthy, and nutrient-rich diet is one of the most effective ways to improve your condition.
Conclusion
Diffuse hair loss is a challenging condition to experience. Not only does it rob you of your confidence, but it can also cause a lot of anxiety, as you suspect an underlying medical condition is at fault.
Because there are many reasons why you’ve developed diffuse thinning, you must visit your doctor as soon as possible.
Only then can you find the root cause of the problem and then look for an effective solution.
While there is no definitive diffuse thinning cure, there are several ways to address the issue and manage symptoms.
Simple lifestyle changes and an effective treatment plan can help reduce, stop and even prevent a diffuse thinning hairline from occurring.
Diffuse Thinning FAQ
Diffuse thinning can sometimes be reversed or improved, especially if it’s caused by reversible factors like stress, nutritional deficiencies, or hormonal imbalances. Treatment effectiveness varies depending on the underlying cause and individual response. Acting in the period of early diffuse thinning stages can often improve outcomes.
Diffuse thinning does not always lead to baldness. Its progression depends on the underlying cause and how it’s managed. In many cases, with appropriate treatment and care, hair loss can be stopped or reversed.
Diffuse thinning can last as long as the underlying cause persists. It may stop if the cause is addressed, such as treating nutritional deficiencies, managing stress, or correcting hormonal imbalances.
Diffuse thinning appears as overall hair thinning across the scalp rather than in distinct patches. The scalp may become more visible, but the hairline typically remains intact.
Diffuse thinning hair can be reversible if it’s caused by temporary factors like stress, illness, medication, or nutritional deficiencies. Once the underlying issue is addressed, hair often regrows over several months.
Stopping diffuse thinning involves identifying and treating the root cause; this could mean improving nutrition, reducing stress, adjusting medications, or using treatments like minoxidil. A dermatologist or trichologist can help determine the best approach.
It depends on the cause—telogen effluvium (stress or illness-related) is usually temporary, while diffuse thinning from genetic hair loss (androgenetic alopecia) can become permanent without treatment. Early intervention improves the chances of preserving and regrowing hair.
Diffuse thinning can often be reversed if treated early by addressing the underlying cause, such as stress, nutritional deficiencies, or hormonal imbalance. Using treatments like minoxidil, improving diet, managing stress, and ensuring adequate protein and iron intake can help restore hair density over time.
Last medically reviewed on October 10th, 2025
- York K, Meah N, Bhoyrul B, Sinclair R. A review of the treatment of male pattern hair loss. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2020 Apr;21(5):603-612. doi: 10.1080/14656566.2020.1721463. Epub 2020 Feb 17. PMID: 32066284.https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32066284/
- Wolff H, Fischer TW, Blume-Peytavi U. The Diagnosis and Treatment of Hair and Scalp Diseases. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2016 May 27;113(21):377-86. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2016.0377. PMID: 27504707; PMCID: PMC4908932.https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27504707/
- Tamashunas NL, Bergfeld WF. Male and female pattern hair loss: Treatable and worth treating. Cleve Clin J Med. 2021 Mar 1;88(3):173-182. doi: 10.3949/ccjm.88a.20014. PMID: 33648970.https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33648970/
- Levine N. Diffuse female hair thinning. Geriatrics. 1996 Aug;51(8):27. PMID: 8707067.https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8707067/
- Levine N. Diffuse thinning of scalp hair. Geriatrics. 2000 Jul;55(7):33. PMID: 10909404.https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10909404/
- Phillips TG, Slomiany WP, Allison R. Hair Loss: Common Causes and Treatment. Am Fam Physician. 2017 Sep 15;96(6):371-378. PMID: 28925637.https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28925637/


