Biotin for Hair Growth: Results, Risks and the Best Supplements

Biotin, also known as B7 and Vitamin H, plays an essential role in converting nutrients in our body into energy.
As an essential B vitamin, it also plays a crucial role in our skin, hair, and nail health.
Biotin supplements can offer an easy way of maximizing the levels of this all-important vitamin and ensuring your hair is getting all the support it needs.
But, like many dietary supplements, there are some things you must consider before taking them.
After all, some lack concrete scientific evidence to support their claims.
Today, we’ll help demystify biotin supplements for you.
We’ll discuss the role it plays in your body, how you can improve your levels naturally, the signs and symptoms of a deficiency, and what supplements we recommend for you to try.
- What is biotin?
- Does it help hair growth?
- When to expect the results
- Before and after
- How much to take
- Risks
- Best foods
- 5 best supplements
- Other benefits
- Deficiency
- Alternatives
What is biotin?
Biotin, also known as vitamin B7 or vitamin H, is a water-soluble vitamin that is part of the B-vitamin family.
It plays a crucial role in the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, and is essential for maintaining the health of hair, skin, and nails.
Vitamin H is often recommended for strengthening hair and nails, and it’s found in a wide variety of foods, including eggs, nuts, seeds, and certain vegetables.
Biotin deficiency is rare, but when it occurs, it can lead to hair loss, skin rashes, and brittle nails.
Does biotin help improve hair growth?
It affects hair growth, shine, texture, volume, and resilience.
It does this by helping the body produce keratin, an essential protein used to create healthy nails, skin, and hair strands.
For this reason, many people want to increase their intake of biotin. However, research is still trying to assert how effective it is as a supplement for treating hair loss.
A study in 2015 examined women experiencing hair loss.
Some were given a protein supplement that contained biotin alongside other ingredients. The other group received a placebo.
Results showed that women who took the supplement twice daily for three months noticed improved hair growth and less hair shedding. A previous study in 2012 had similar results.
But because the supplement contained other ingredients, researchers could not say conclusively whether biotin supplementation influenced the women’s hair loss on its own, or not.

How long does it take for biotin to work?
It may take a few months or longer for increased levels of biotin in your body to pay off. You will need to be patient and committed.
An easy way to maximize this vitamin in your body is by improving your diet and concentrating on foods rich in biotin.
Nuts, seeds, legumes, and leafy greens are some excellent examples.
It’s important to note that increased biotin in your system does not automatically mean your hair loss will stop – it will only have an impact if you’re currently suffering from a deficiency.
Furthermore, be careful not to consume too much, as there are some side effects, and it won’t speed up the process anyway.
If in doubt, visit your doctor or skin specialist for advice.
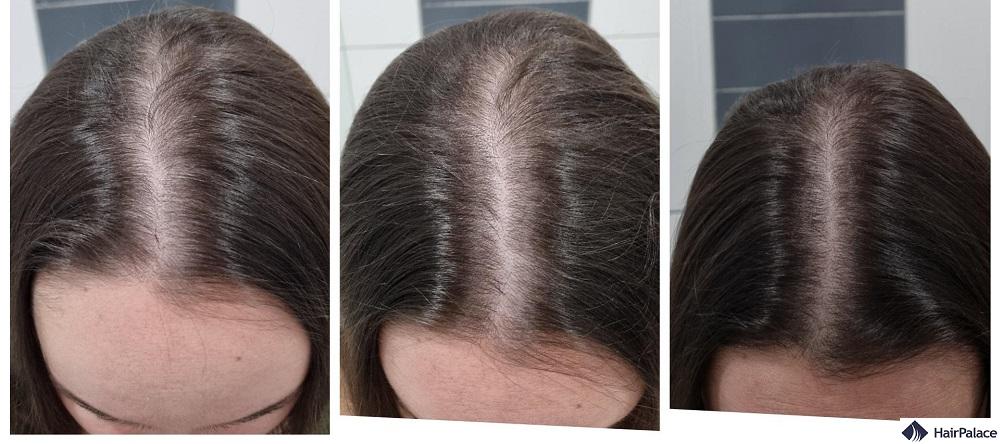
Biotin hair growth before and after pictures
How much biotin should you take a day?
The recommended dietary allowance (RDA) is a common way to gauge how much of a nutrient we need in our diet.
It is set by the Food and Nutrition Board at the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine.
But when there isn’t enough scientific evidence to recommend an RDA, an ‘Adequate Intake’ (AI) is issued instead, as is the case for biotin.
The AI for biotin for men and women over 19 is 30 mcg. It is 35 mcg for women who are breastfeeding.
The NHS suggests that we may get all the biotin we need from a well-balanced diet and that taking .9 mg daily is unlikely to cause any adverse side effects.

Can you take too much biotin?
As with all nutrients and vitamins, there is a limit to how much your body should be intaking. But because it is a water soluble B vitamin, it is rare to overdose on biotin supplements.
That said, it is possible.
Symptoms of taking too much biotin include:
- Skin rashes
- Excessive thirst
- Excessive urination
- Insomnia
- Low levels of other vitamins in your system, including Vitamins C and B6
- A drop in insulin
- High blood sugar levels
Does biotin have side effects?
Most people can take biotin for thinning hair and experience no adverse side effects.
But a rare few may experience nausea, diarrhoea, or stomach cramping.
If you suffer from any of those three, it may be wise to take your supplements with food to minimize and counteract symptoms.
As always, consult your doctor when taking a dietary supplement, and always read the manufacturer’s labels and recommended dosage carefully.
The best foods to increase your biotin intake
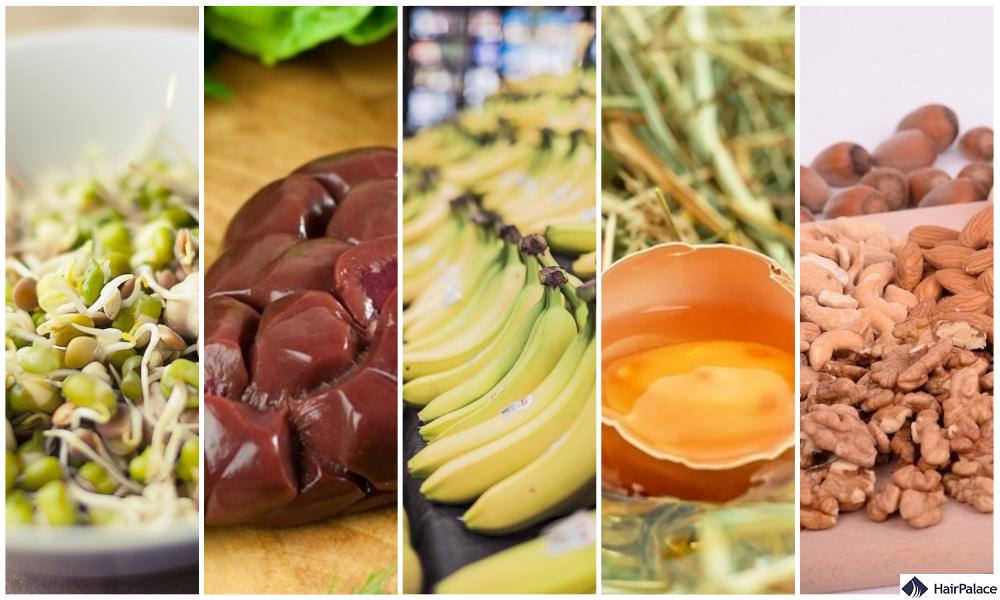

More often than not, your body is getting enough biotin from your average diet.
But if you want to increase your intake and ensure you’re reaching your ideal target, there are many foods that we highly recommend.
Biotin-rich foods for hair growth include:
- Nuts and seeds like almonds, peanuts, and sunflower seeds
- Meat, especially kidney and liver
- Fish
- Egg yolks and raw egg whites
- Mushrooms
- Bananas
- Sweet potatoes
- Whole grains
For average nutritional values, take a look at the best sources of biotin infographic below:
| Food item | Biotin content | Daily value |
|---|---|---|
| Egg yolk (50 grams) | 10 mcg | 33% |
| Mushroom (70 grams) | 5.6 mcg | 19% |
| Chicken liver (75 grams) | 138 mcg | 460% |
| Salmon (85 grams) | 5 mcg | 17% |
| Banana (105 grams) | 0.2 mcg | 1% |
| Avocado (200 grams) | 1.85 mcg | 6% |
| Sweet potatoes (125 grams) | 2.4 mcg | 8% |
| Pork chop (85 grams) | 3.8 mcg | 13% |
| Spinach (64 grams) | 5 mcg | 17% |
It’s important to remember that biotin levels may vary between different food brands; check packaging and labels for exact nutritional amounts.
Another tip is preparation – or lack thereof in the case of biotin. Heat can often compromise the vitamin’s effectiveness, so whenever possible, eat foods raw.
That said, chances are you are reaching your biotin levels perfectly fine, so long as you follow a well-balanced diet, you should reach any and all targets of dietary reference intakes.

5 best biotin supplements
Taking biotin tablets for hair growth may give you the peace of mind that your hair is getting all the resources it needs to grow strong.
They can be bought over the counter, without a prescription, and come in tablets or capsules.
As with any potential nutritional deficiencies, consult your doctor and read the packaging and directions carefully before use.
Below are 5 of the best supplements for you to consider, including their price, recommended dosage, and amount per product.
| Biotin supplement | Price | Amazon Ratings | Count per bottle | Biotin dosage | Vegan |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Country Life High Potency Biotin | £18.40 | 60 capsules | 5000 mcg | ||
| Pure Encapsulations Biotin | £22.35 | 120 capsules | 8000 mcg | ||
| Life Extension Biotin | £7.50 | 100 capsules | 600 mcg | ||
| SugarBear Hair Vitamin | £30.90 | 75 gummies | 5100 mcg | ||
| OLLY Heavenly Hair Gummy | £13.50 | 60 gummies | 3000 mcg |
Biotin shampoo for hair growth?
Using a biotin hair growth shampoo can be beneficial, particularly for individuals looking to improve the health and appearance of their hair.
Biotin, being a key nutrient for healthy hair, may help strengthen hair, reduce breakage, and improve overall hair quality when used in topical products like shampoos.
However, it’s important to note that while biotin shampoos can support hair health, they may not directly cause significant hair growth, especially in cases of genetic hair loss.
Other biotin benefits
Other than using biotin for hair loss, taking supplements might also yield other benefits, including:
- Metabolism: Can support a healthy metabolism, i.e., converting food into energy.
- Amino Acids: It helps produce proteins that play a key role in fatty acid synthesis (energy storage).
- Reducing Inflammation: Alleviates stress and pain from muscle joints
- Cognition: It can also improve memory and prevent cognitive issues and neurodegenerative disorders.
- HDL: Biotin can remove excess cholesterol in the body (high-density lipoprotein)
- LDL: It can help reduce bad cholesterol in arteries (low-density lipoprotein)
Biotin deficiency
There are several symptoms related to biotin deficiency. After all, as a B vitamin, it plays a crucial role in several areas of our body.
You may only be experiencing a marginal deficiency that can be easily corrected.
If you notice any of the following, you must consult your healthcare provider for a formal diagnosis.
- Biotin hair loss
- Brittle nails
- Dry skin
- Red, scaly rashes appear, especially around your face.
- Depression
- Tiredness and exhaustion
- Conjunctivitis
- Hallucinations
- Exhaustion
- A tingling or numb sensation in your arms and legs

Who may be at risk for a biotin deficiency?
Some people may be at a higher risk of developing a deficiency. They include:
- Biotinidase deficiency: This is a genetic disorder affecting biotin metabolism, inhibiting its reuse or recycling ability. Many countries screen for the disorder at birth.
- Alcoholism: If you suffer from alcoholism, you may have a deficiency. This is because long-term alcohol inhibits your ability to absorb biotin.
- Malnutrition: A poor diet can lead to vitamin deficiencies, including biotin.
- Inflammatory bowel disease: Conditions like Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis can reduce biotin levels in your body, affecting your gut’s natural ability to produce it.
- Smoking: The American Food and Nutrition Board has said that smoking accelerates biotin catabolism, leading to lower levels in your body.
A reduction in biotin levels can result from pregnancy or breastfeeding. New mothers may suffer a decrease despite their diet.
Additionally, some medications can increase your chances of developing a deficiency. Two in particular include:
- Retinoids are compounds derived from Vitamin A, often used to treat skin disorders like acne, psoriasis, rashes, and dermatitis., or antiepileptics (for seizures),
- Antiepileptics are medications used to treat seizure disorders, nerve pain, and mental health conditions like bipolar personality disorder.
Aside from the above examples, taking a supplement or receiving biotin treatment without a deficiency may not affect hair regrowth at all.
What else can you try to stimulate hair growth?
Besides supplementation, several other viable options can help promote hair growth and restore it to its former glory. Some of the most popular include:
- Scalp massages
- Caffeine shampoo
- Essential oils
- Hair growth products
That said, the above alternatives only offer a temporary solution. You should consider hair transplantation if you’re serious about treating hair loss and want a permanent solution.
A hair transplant is a cutting-edge procedure that creates a seamless, natural-looking hairline.
The most popular technique is undoubtedly the FUE hair transplant, which offers a quick recovery and no visible scarring.
The FUE2 is an advanced procedure form with an impressive success rate of up to 95%.
FAQ
The recommended daily intake for adults is around 30 micrograms. However, this can vary based on age, health status, and other factors. Pregnant or breastfeeding women may require higher amounts. It’s always best to consult with a healthcare provider for personalized recommendations.
Biotin is good for supporting the health of hair, skin, and nails, aiding in metabolism, and helping to convert food into energy. It is also important for the functioning of the nervous system.
Vitamin B7.
Vitamin B7 helps in metabolizing fats, carbohydrates, and proteins, supports healthy hair, skin, and nails, and aids in energy production.
The recommended daily intake for hair growth is typically 2,500 to 10,000 mcg, but most people get enough from their diet.
Biotin can take 2 to 6 months of consistent use to show noticeable hair growth improvements.
Biotin helps with keratin production and hair growth, while collagen supports scalp health and hair strength. Both can be beneficial, but collagen is often better for overall hair thickness and structure.
High doses of biotin (above 10,000 mcg daily) are generally safe but may cause skin breakouts, and digestive issues, and interfere with lab tests.
Last medically reviewed on March 13th, 2025
- Aldahmash BA, et al. (2015). Biotin amelioration of nephrotoxicity in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. DOI:https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1319562X15000613
- Lazo-de-la-Vega-Monroy, M-L, et al. (2017). Effects of dietary biotin supplementation on glucagon production, secretion, and action. DOI:https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28935144/
- NHS (2020), B vitamins and folic acidhttps://www.nhs.uk/conditions/vitamins-and-minerals/vitamin-b/
- Biotin. (n.d.).https://lpi.oregonstate.edu/mic/vitamins/biotin